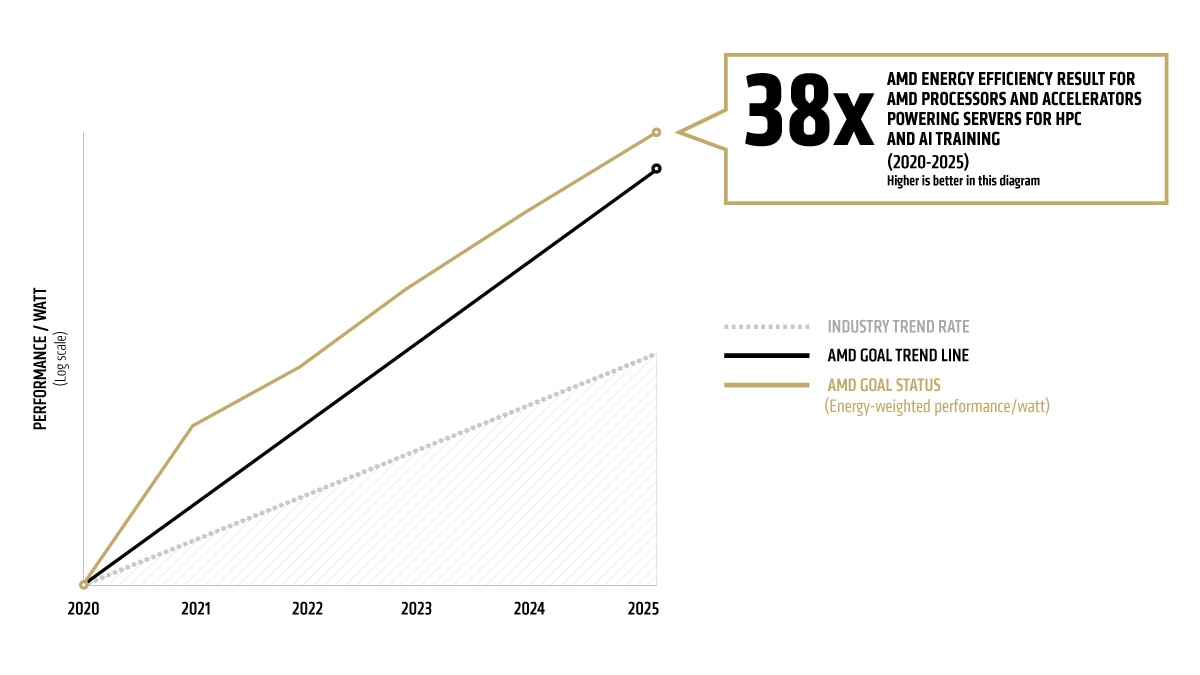
together we advance_environmental sustainability
Accelerating the Renewable Energy Transition in the Supply Chain
AMD is a sponsor and steering committee member of the SEMI Energy Collaborative (EC), working with industry leaders to expand access to low-carbon energy in Asia Pacific. In 2024-25, AMD directly engaged with EC leadership, member companies and policymakers to address market barriers and strategies to support the clean energy transition.