AMD Delivering Open Rack Scale AI Infrastructure
Jun 12, 2025

At a Glance:
- Agentic AI is driving higher demands across the stack—requiring not just powerful GPUs, but also high-performance CPUs and secure, efficient networking. To support these multi-agent workflows, optimized coordination between AMD Instinct™ GPUs, AMD EPYC™ CPUs, and Pensando™ NICs is essential for performance, scalability, and security.
- AMD and partners are delivering the open standard AI Rack infrastructure with an up to 128-GPU rack in market built around AMD Instinct™ MI350 series GPUs, 5th Gen EPYC™ CPUs and Pensando™ Pollara 400 NICs.
- AMD previewed the next major step in its AI solutions roadmap, introducing “Helios” – a reference design solution based on AMD Instinct MI400 GPUs, AMD EPYC “Venice” CPUs and Pensando “Vulcano” AI NICs to support the most demanding AI workloads
A Proven Foundation – Available Today
Agentic AI represents the next wave of AI transformation, one where intelligent agents not only automate tasks but drive complex workflows, innovation, and decision-making across industries. These agents rely on a network of interconnected models, applications, and data, demanding more than just GPU horsepower. They need high-performance CPUs to orchestrate tasks, secure data flows across the network, and manage enterprise-grade workloads seamlessly. AMD is uniquely positioned to power every layer of this stack—from Instinct™ GPUs and EPYC™ CPUs to Pensando™ DPUs and scale-out networking—all underpinned by open, flexible, and programmable infrastructure designed for modern AI.
At AMD we know that Agentic AI isn’t just a vision or a concept, it is here today. Our customers want it, the industry is demanding it, and we are enabling it with our leadership portfolio of products and our open-standard rack infrastructure.
To deliver leadership performance at scale, you need more than a powerful GPU, you need a modern, open rack architecture purpose-built for AI – and you get that with 5th Gen AMD EPYC CPUs, the AMD Instinct MI350 Series GPUs, and scale-out networking solutions including AMD Pensando Pollara AI NIC, all integrated into an industry-standard OCP and Ultra Ethernet Consortium compliant design.
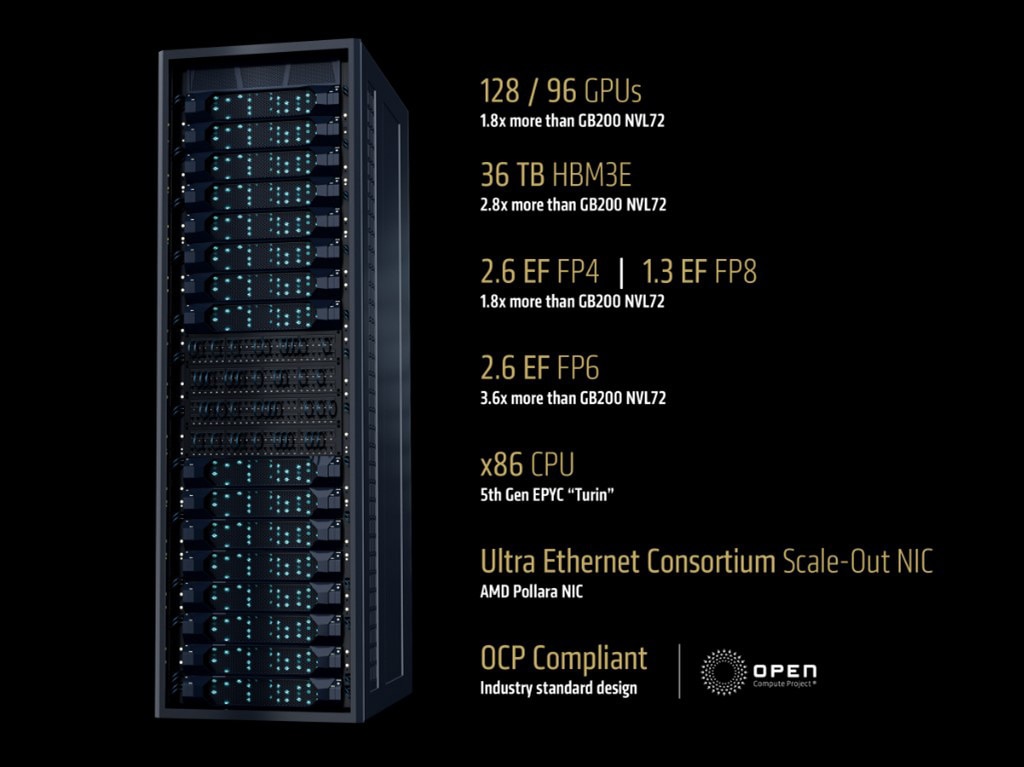
These racks are built on OCP-compliant reference designs and help ensure interoperability and seamless integration with existing OCP compliant infrastructure, giving our CSP partners and enterprise customers the choice they need that is readily available from the OEM and ODM partners they know.
How are we doing this? With our four guiding principles:
- Leadership Compute Performance: Instinct MI350 Series GPUs deliver exceptional inference and training performance from the highest memory capacity, up to 36TB of HBM3E in a 128 GPU rack2, and up to 1.6x more FP6 performance than the competition1.
- Enterprise-Grade CPUs: 5th Gen EPYC™ processors provide an industry standard, x86 host processor, for seamless interface to existing enterprise applications.
- Advanced Networking: AMD Pensando Pollara NICs, the industry’s first UEC-ready AI NIC, combines programmable transport, path-aware congestion control, and intelligent packet spraying to deliver leading performance for the largest AI clusters
- Open Standards and Design: Supporting open standards such as Ultra Ethernet Consortium and open holistic design from the Open Compute Project
By combining all our hardware components into a single rack solution, we are enabling a new class of differentiated, high-performance AI infrastructure in both liquid and air-cooled configurations.
Introducing Next-Generation AMD AI Rack Infrastructure: “Helios”
The future of AI demands more integration, more compute, and seamless capabilities that blend compute engines, software and more. And we are doing that with, “Helios.”
We are aligning our silicon, software, and systems expertise to deliver a fully integrated AI rack platform that is engineered with scale-up and scale out capabilities to deliver leadership performance in both large-scale training and distributed inference. This is more than a next-generation upgrade, “Helios” redefines what is possible at the rack level.
“Helios” is a reference design built to deliver the compute density, memory bandwidth, performance and scale out bandwidth needed for the most demanding AI workloads, in a ready-to-deploy solution that accelerates time to market. From training the next wave of frontier models, to running distributed inference at scale and fine-tuning enterprise models on proprietary business data, “Helios” is designed to do it all - with openness, efficiency and unmatched flexibility.
This solution integrates a powerful combination of the next generation of AMD technology including:
- Next-Gen AMD Instinct MI400 Series GPUs. Expected to offer up to 432 GB of HBM4 memory, 40 petaflops of MXFP4 performance and 300 gigabytes per second of scale-out bandwidth3. These GPUs will bring rack-scale AI performance leadership for training massive models and running distributed inference at scale.
- Open Scale-Up with UALink™. With the “Helios” reference design, performance scales effortlessly across 72 GPUs—thanks to UALink. The UALink standard is an open standard that will enable customer choice and interoperability in scale up fabrics. In “Helios,” we use UAL in several ways, to interconnect the GPUs and scale-out NICs, and, tunneled over ethernet, to interconnect the GPUs. This connects every GPU in the rack, enabling them to communicate as one unified system—delivering breakthrough performance at rack scale.
- 6th Gen AMD EPYC "Venice" CPU. Powered by the groundbreaking "Zen 6" architecture, the CPUs are expected to offer up to 256 cores, up to 1.7X the performance4 and 1.6 TBs of memory bandwidth5 to help sustain maximum performance across the entire “Helios” rack.
- AMD Pensando "Vulcano" AI NICs. The next-generation NIC for AI scale out is UEC 1.0 compliant and supports both PCIe® and UALink interfaces for direct connectivity to CPUs and GPUs. It will also support 800G network throughput and an expected 8x the scale-out bandwidth per GPU3 compared to the previous generation. “Vulcano” is crucial for enabling rapid and seamless data transfer within high-density clusters, effectively eliminating communication bottlenecks for large-scale AI deployments.

“Helios” is our step to the future; it represents open standards, heterogeneous compute, and a commitment to developer-first innovations that extend AI beyond the data center. We’ll have more to share in 2026, but we’re very excited for “Helios” and what it will do.
Customer Spotlight: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Adoption of AMD AI Solutions
What’s more important is that we have critical partners that are joining us on this journey to creating the next generation of AI Rack Scale compute.
Oracle will be among the first industry leaders to adopt the AMD Instinct MI355X-powered rack-scale solution, underlining their commitment to providing one of the broadest AI infrastructure offerings. This adoption is particularly impactful, as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure supports a wide range of mission-critical enterprise workloads with stringent requirements for scalability, reliability, security, and performance. Oracle's deployment highlights the tangible value that AMD solutions bring to enterprise-level generative and agentic AI applications for customers globally.
Mahesh Thiagarajan, executive vice president, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
“Oracle Cloud Infrastructure continues to benefit from its strategic collaboration with AMD. We will be one of the first to provide the MI355X rack-scale infrastructure using the combined power of EPYC, Instinct, and Pensando. We've seen impressive customer adoption for AMD-powered bare metal instances, underscoring how easily customers can adopt and scale their AI workloads with OCI AI infrastructure. In addition, Oracle relies extensively on AMD technology, both internally for its own workloads and externally for customer-facing applications. We plan to continue to have deep engagement across multiple AMD product generations, and we maintain strong confidence in the AMD roadmap and their consistent ability to deliver to expectations.”
The AMD Optimized AI Solutions
We’ve extended our solution engineering from the node to the rack and to the cluster level, addressing the scale needed for autonomous agents. Our commitment to open-standards innovation, a strong partner ecosystem, and aggressive investment in our capabilities puts us at the center of solution integration.
With the AMD open rack-scale AI solution, we’re giving customers ready to deploy infrastructure that’s ready right now. And with “Helios,” AMD continues our tradition of elevating AI infrastructure to unprecedented levels.

Related Blogs
Footnotes
- MI350-026A - Based on calculations by AMD Performance Labs in September 2025, for the 128 GPU AMD Instinct MI355X rack to determine the peak theoretical precision performance when comparing FP64, FP32, FP16, OCP FP8, FP8, MXFP6, FP6, MXFP4 and FP4 datatypes with Matrix, Tensor, Vector, and Sparsity, as applicable vs. a similarly configured NVIDIA Grace Blackwell GB200 NVL72 72 GPU rack. Server manufacturers may vary configurations, yielding different results. Results may vary based on the use of the latest drivers and optimizations.
- MI350-027 - Calculations by AMD Performance Labs in May 2025, based on the published memory capacity specifications of AMD Instinct MI350X / MI355X OAM 128xGPU rack vs. an NVIDIA Blackwell GB200 72xGPU (NVL72) rack. Server manufacturers may vary configurations, yielding different results. Results may vary based on the use of the latest drivers and optimizations.
- GD-247A: Preliminary performance estimates based on AMD engineering projections or early measurements as of June 2025, and subject to change.
- VEN-001: SPECrate®2017_int_base comparison based on AMD internal estimates for top of stack 2P 6th Gen EPYC CPU and 5th Gen EPYC measurements as of 6/3/2025. Preliminary performance estimates based on AMD engineering projections or measurements as of June 6, 2025, and subject to change.
- VEN-003: PCIe Gen comparison based on PCI-SIG published statements, https://pcisig.com/pci-express-6.0-specification. 2P 6th Gen EPYC CPU with 128 lanes of PCIe Gen 6 and 5th Gen EPYC with 128 lanes of PCIe Gen 5 as of 6/3/2025. PCIe is a registered trademark of PCI-SIG Corporation
- MI350-026A - Based on calculations by AMD Performance Labs in September 2025, for the 128 GPU AMD Instinct MI355X rack to determine the peak theoretical precision performance when comparing FP64, FP32, FP16, OCP FP8, FP8, MXFP6, FP6, MXFP4 and FP4 datatypes with Matrix, Tensor, Vector, and Sparsity, as applicable vs. a similarly configured NVIDIA Grace Blackwell GB200 NVL72 72 GPU rack. Server manufacturers may vary configurations, yielding different results. Results may vary based on the use of the latest drivers and optimizations.
- MI350-027 - Calculations by AMD Performance Labs in May 2025, based on the published memory capacity specifications of AMD Instinct MI350X / MI355X OAM 128xGPU rack vs. an NVIDIA Blackwell GB200 72xGPU (NVL72) rack. Server manufacturers may vary configurations, yielding different results. Results may vary based on the use of the latest drivers and optimizations.
- GD-247A: Preliminary performance estimates based on AMD engineering projections or early measurements as of June 2025, and subject to change.
- VEN-001: SPECrate®2017_int_base comparison based on AMD internal estimates for top of stack 2P 6th Gen EPYC CPU and 5th Gen EPYC measurements as of 6/3/2025. Preliminary performance estimates based on AMD engineering projections or measurements as of June 6, 2025, and subject to change.
- VEN-003: PCIe Gen comparison based on PCI-SIG published statements, https://pcisig.com/pci-express-6.0-specification. 2P 6th Gen EPYC CPU with 128 lanes of PCIe Gen 6 and 5th Gen EPYC with 128 lanes of PCIe Gen 5 as of 6/3/2025. PCIe is a registered trademark of PCI-SIG Corporation








