UltraFast™ Embedded Design Methodology Guide
This guide is organized around important functional areas that map to specific skill sets within development teams.

The AMD embedded software ecosystem empowers developers to accelerate their journey from an idea to market-ready deployable embedded systems. With a comprehensive suite of tools, runtimes, environments, and solution stack, this ecosystem is tailored to seamlessly harness the capabilities of the AMD embedded product portfolio of devices, including AMD Zynq™ 7000 SoCs, Zynq UltraScale+™ MPSoCs, and Versal™ adaptive SoCs, and MicroBlaze™ and MicroBlaze V processor cores.
With the introduction of the new AMD Embedded Development Framework (EDF), AMD offers a complete, modular, open-source environment built on the industry-standard Yocto Project™. EDF provides feature-rich prebuilt images, automated flows, and different design entry points that help embedded developers to reduce development cycles and accelerate time to market.
In addition, EDF is built on a foundation of advanced features, including pioneering security and virtualization software drivers that are intricately woven into the fabric of Zynq and Versal devices. This synergy unlocks the potential to craft ingenious, interconnected, and distinct systems that meet the demands of modern embedded applications.
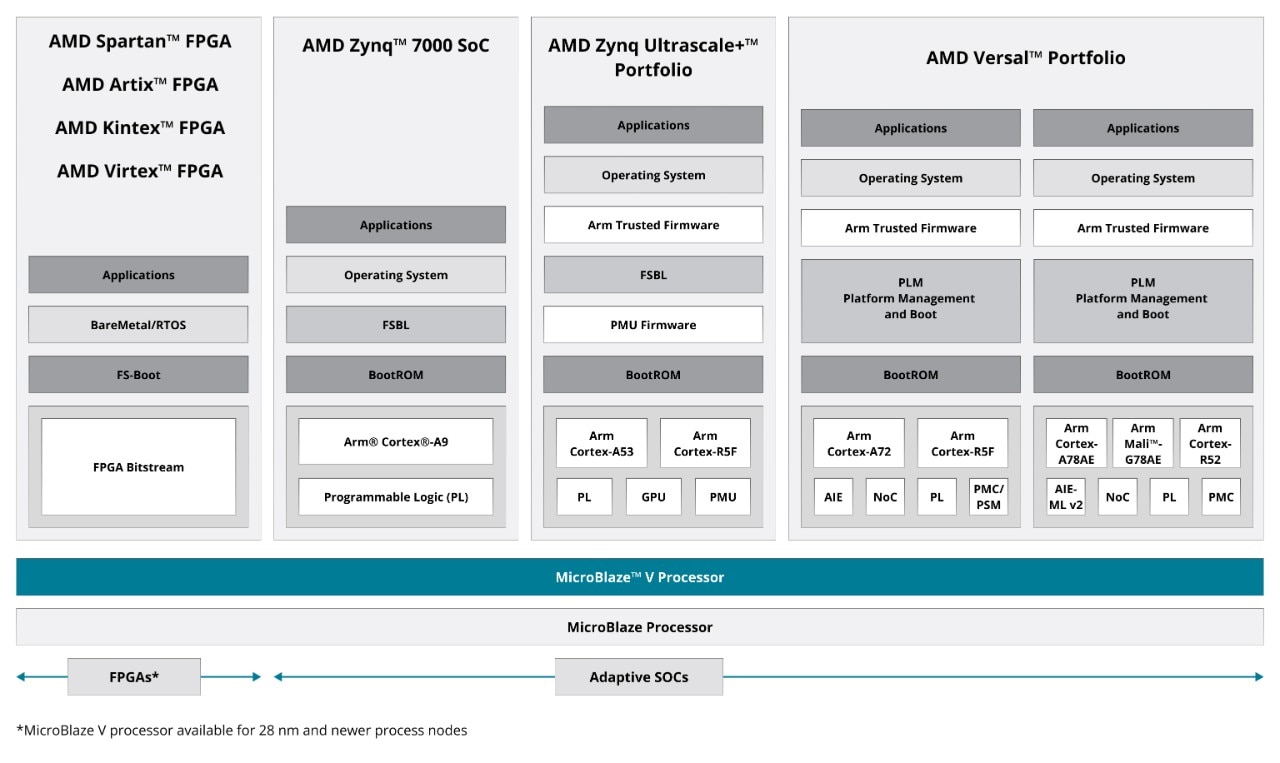
Linux® is the most prevalent operating system used by AMD products. AMD provides EDF Linux OS and the Embedded Development Framework (EDF), a Yocto Project™ based environment and Linux distribution, which includes source code and Yocto recipe files from our GIT repository, enabling Linux support for AMD silicon through in-house build systems or third-party tools. EDF Linux OS is a customized, non-commercial Linux development project designed for development on AMD Versal™ adaptive SoCs, Zynq™ UltraScale™ MPSoCs, Zynq 7000 SoCs, and MicroBlaze™ processors.
The Linux kernel support in AMD EDF releases tracks the LTS Kernel.
AMD currently offers two tools to build and deploy embedded Linux solutions. The first is AMD EDF, built on the open-source Yocto Project™, and the second is PetaLinux, which is being superseded by AMD EDF. Both tools provide a quick way to build an embedded Linux image, with EDF also supporting more advanced use cases.
AMD Open-Source Linux Flows:
The AMD Vitis™ unified software platform, Software Development Kit (SDK), and ecosystem partner tools offer a wide choice of development environments that enable SoC-like C/C++ programming of the Zynq and Versal platforms.
RTOS, Hypervisors, and Bare-Metal
The Zephyr Project is a scalable real-time operating system (RTOS) supporting multiple hardware architectures, optimized for resource constrained devices, and built with security in mind.
The Zephyr OS is based on a small-footprint kernel designed for use on resource-constrained systems: from simple embedded environmental sensors and LED wearables to sophisticated smart watches and IoT wireless gateways.
More information about Zephyr Project can be found at: https://www.zephyrproject.org/
AMD’s Zephyr Project repository can be found at: https://github.com/Xilinx/zephyr-amd
FreeRTOS is a market-leading RTOS from Amazon Web Services that supports more than 35 architectures and was downloaded once every 3 minutes during 2017. It is professionally developed, strictly quality controlled, robust, supported, and free to embed in commercial products without any requirement to expose your proprietary source code (reference: https://www.freertos.org/RTOS.html).
More information on FreeRTOS can be found at https://www.freertos.org/RTOS.html.
More information and support resources for FreeRTOS on AMD products can be found at AMD FreeRTOS
| Processor | Device |
|---|---|
| 64-bit Arm® Cortex®-A72 application processor unit (APU) & 32-bit Cortex-R5 real-time processor unit (RPU) | Versal adaptive SoCs |
| 64-bit Arm Cortex-A53 application processor unit (APU) & 32-bit Cortex-R5 real-time processor unit (RPU) | Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoCs & Kria™ SOMs |
| 32-bit Arm Cortex-A9 application processor unit (APU) | Zynq 7000 SoC devices |
| 32-bit MicroBlaze processor | All AMD device families |
| Provider | Product | Zynq 7000 SoC | Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC | Versal Adaptive SoC | MicroBlaze | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex-A9 | Cortex-A53 | Cortex-R5 | VCU | Mali-400 | Cortex-A72 | Cortex-R5F | AIE | |||
| AMD | Bare-Metal | Y | Y1 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| AMD | FreeRTOS | Y | Y1 | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| AMD | Zephyr6 | N | Y4 | Y4 | Y4 | Y4 | ||||
| BlackBerry | QNX Neutrino | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| QNX OS for Safety | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | |
| Wind River | VxWorks | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N |
| Green Hills | INTEGRITY-178 | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N |
| INTEGRITY | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | |
| u-velOsity | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y3 | N | N | |
| Siemens | Nucleus | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y4 | N | N |
| PX5 | PX5 RTOS | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y |
| Microsoft | Azure RTOS | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y |
| ETAS | ETAS RTA-OS | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Sysgo | PikeOS | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| PikeOS for MPU | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | |
| Lynx | LynxOS-178 | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Weston Embedded | Cesium Cs/OS2, OS3 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| DDC-I | Deos | Y | Y | N |
N | N | N | N | N | N |
| RTEMS | RTEMS | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y |
| eForce | uC3 | Y1 | Y1 | N |
N | N | N | N | N | N |
| ENEA | OSE | Y | Y | N |
N | N | N | N | N | N |
| eSOL | eT-kernel | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Silicon Labs | Micrium uc/OS-II / OS-III5 | Y | Y1 | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Sciopta | Sciopta RTOS | Y1 | Y1 | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Wittenstein | SafeRTOS | Y1 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Segger | emBOS | Y1 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
Most RTOS provide some level of certification for different safety standards. Please consult with the OS vendor to determine if it needs your specific needs.
More information and support resources can be found at the AMD Wiki: Embedded Software Ecosystem.
AMD provides its customers and partners with key technologies, documentation, and support to enable advanced, multi-OS system designs on our products. Offerings available from our ecosystem include:
| Vendor | Product | Versal Adaptive SoC | Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC | Zynq 7000 SoC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD | Xen Hypervisor | Y | Y | N |
| BlackBerry | QNX Hypervisor | Y | Y | N |
| Wind River | Helix Virtualization Platform | Y | Y | N |
| Sysgo | PikeOS Hypervisor | N | Y | Y |
| Green Hills | Integrity Multivisor | Y1 | Y1 | N |
| Lynx | LynxSecure Separation Kernel Hypervisor | Y | Y | N |
| Dornerworks | SEL4 | Y | Y | N |
| Siemens | Nucleus Hypervisor | N | Y | Y |
| General Dynamics Mission Systems | OKL4 Microvisor | N | Y | N |
More information and support resources can be found at the AMD Wiki: Embedded Software Ecosystem.
AMD provides additional libraries and bare-metal drivers. These libraries are developed specifically for AMD devices.
More information and support resources for bare-metal drivers and libraries can be found at the AMD Wiki: Bare-Metal and Libraries.
Open-source Linux is the most popular operating system to run on embedded hardware, and AMD has been providing support for Linux on their FPGA and adaptive SoC devices since the introduction of the AMD Virtex™ II Pro FPGA in 2001. As well as PetaLinux and Yocto build environments, AMD provides commercial support for targeting AMD devices from several third-party vendors, including Certified Ubuntu® by Canonical Ltd.
As the Yocto Project states: “The Yocto Project is an open-source collaboration project that helps developers create custom Linux-based systems for embedded products, regardless of the hardware architecture. The project provides a flexible set of tools and a space where embedded developers worldwide can share technologies, software stacks, configurations, and best practices that can be used to create tailored Linux images for embedded devices.” The AMD Embedded Development Framework is based on the Yocto Project.
Both flows offer everything necessary to customize, build, and evaluate embedded Linux solutions on AMD processing systems. Tailored to accelerate design productivity, the solution works with the AMD hardware design tools to ease the development of Linux systems for Versal adaptive SoCs, Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoCs, Zynq 7000 SoCs, and MicroBlaze processors. However, the PetaLinux tools have now been superseded by AMD EDF. Please see the AMD PetaLinux Tools page for more information:
| Provider | Product | Distribution | Versal Adaptive SoC | Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC | Zynq 7000 SoC | MicroBlaze |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD | AMD EDF | Yocto | Y | Y | Y | Y* *MicroBlaze V only |
| PetaLinux | Yocto | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Yocto | Yocto | Y | Y | Y | Y | |
| Canonical | Ubuntu | Debian | Y1 | Y | N | N |
| Wind River | Wind River Linux | Yocto | Y | Y | Y | N |
| Foundies.io | FoundriesFactory | Yocto | Y | Y | N | N |
| Siemens | Sokol Flex OS | Yocto | N | Y | Y | N |
| Sokol Omni OS | Debian | N | Y | N | N | |
| TimeSys | Linux Services | Yocto | Y | Y | Y | N |
| MontaVista | CGX/CGE | Yocto | N | Y | Y | N |
| ArchLinuxARM | ArchLinuxARM | N/A | N | N | Y | N |
More information and support resources can be found at the AMD Wiki: Embedded Software Ecosystem.
QEMU (Quick EMUlator) is an open-source, cross-platform, system emulator. It is an executable that runs on an x86 Linux operating system. QEMU can emulate a full system (commonly referred to as the guest), such as an AMD ZCU102 or VCK190 board.
The emulation includes the processors, peripherals, and other hardware on the development board—allowing you to launch an operating system or other applications on the virtualized hardware.
QEMU can also interact with the host machine through interfaces, such as CAN, Ethernet, and USB—enabling real-world data from the host to be used in the guest machine in real time.
Xen is a Type 1 hypervisor defined, maintained, and provided to the open-source community by the Xen Project. Xen allows multiple instances of operating system(s) or bare-metal applications to execute on AMD Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoCs. Additional information on the Xen hypervisor can be found at the Xen Project Getting Started page.
U-Boot is an open-source Universal Boot Loader that is frequently used in the Linux community. AMD provides a GIT tree located at https://github.com/Xilinx/u-boot-xlnx, that includes a U-Boot to run on AMD boards.
Arm Trusted Firmware provides a reference to secure software for the ARMv8-A architecture as well as implementations of various interface standards like PSCI (Power State Coordination Interface) and Secure monitor code for interfacing to normal world software. The AMD Arm Trusted Firmware port is released and available at https://github.com/Xilinx/arm-trusted-firmware.