Article Number: DH-012
AMD Radeon Settings allows users to adjust image quality and the level of detail in games. Since higher visual quality may impact performance, achieving an optimal gaming experience requires balancing visual quality and performance. For most users, the default driver settings offer the best mix of visual quality and performance, measured in frames per second (FPS).
Accessing Radeon Settings Gaming Options
To access these options open AMD Radeon Settings by right clicking on your desktop and select AMD Radeon Settings.
Click on the Gaming Tab.
Click on Global Settings.
Note! Any changes made in global settings should apply to all 3D applications upon launch.
If you wish to create customised settings for specific 3D applications, you can create individual application profiles. This is explained in the Creating Application Profiles section of this document.
Anti-Aliasing Method
Anti-Aliasing (AA) improves image quality by reducing jagged edges from textures.
Applying AA can make an image look smoother and softer, at the expense of lowering FPS.
In the example below, the image on the left has AA applied. The image on the right has no AA applied and has more jagged edges.

Radeon Settings offers three AA types and each has different characteristics and performance cost.
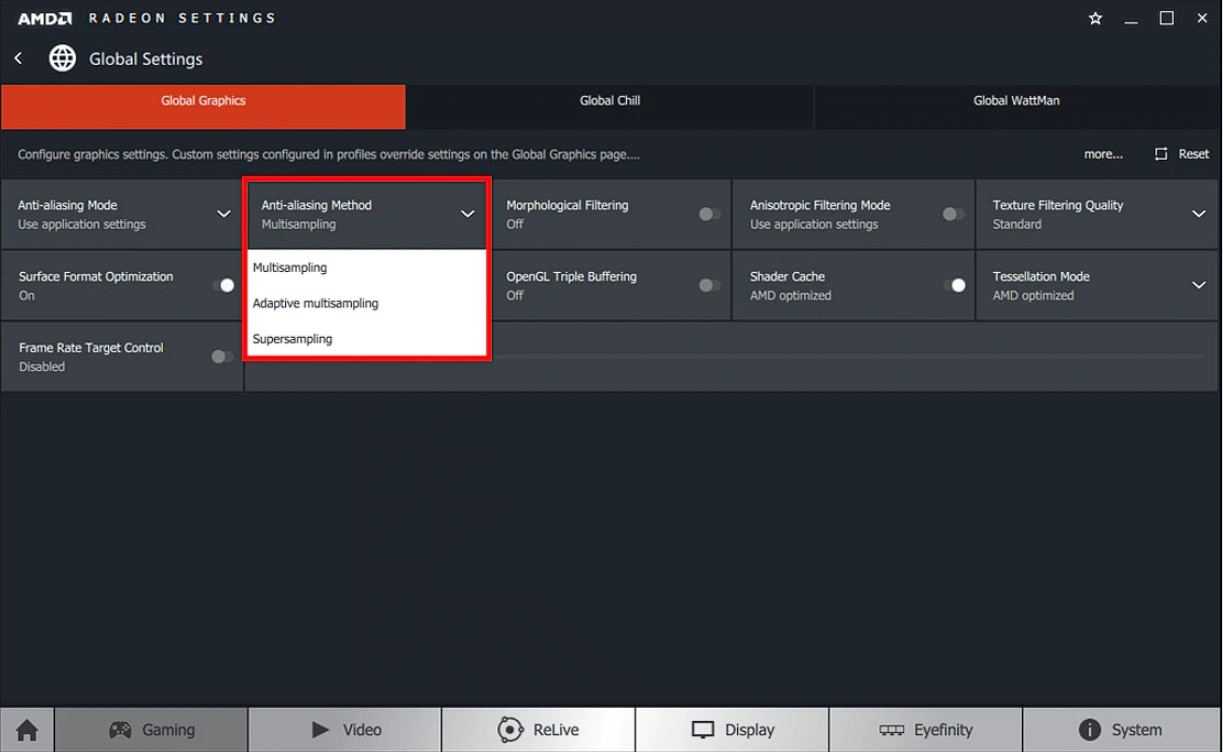
Selecting Anti-Aliasing Mode enables three options:
- Multisampling Anti-Aliasing (MSAA): MSAA improves image quality by reducing aliasing at the edge of textures, however it cannot remove aliasing on transparent textures such as fences.
- Adaptive Anti-Aliasing (AAA): AAA improves image quality by reducing aliasing at the edge of textures and from transparent textures.
- Sparse Grid Supersampling Anti-Aliasing (SSAA): SSAA improves image quality by taking more samples than MSAA and AAA, reducing aliasing from all textures. SSAA has the highest impact on FPS of all AA settings within Radeon Settings.
Anti-Aliasing Mode
Anti-Aliasing Mode determines whether AA is controlled via the 3D application or Radeon Settings.
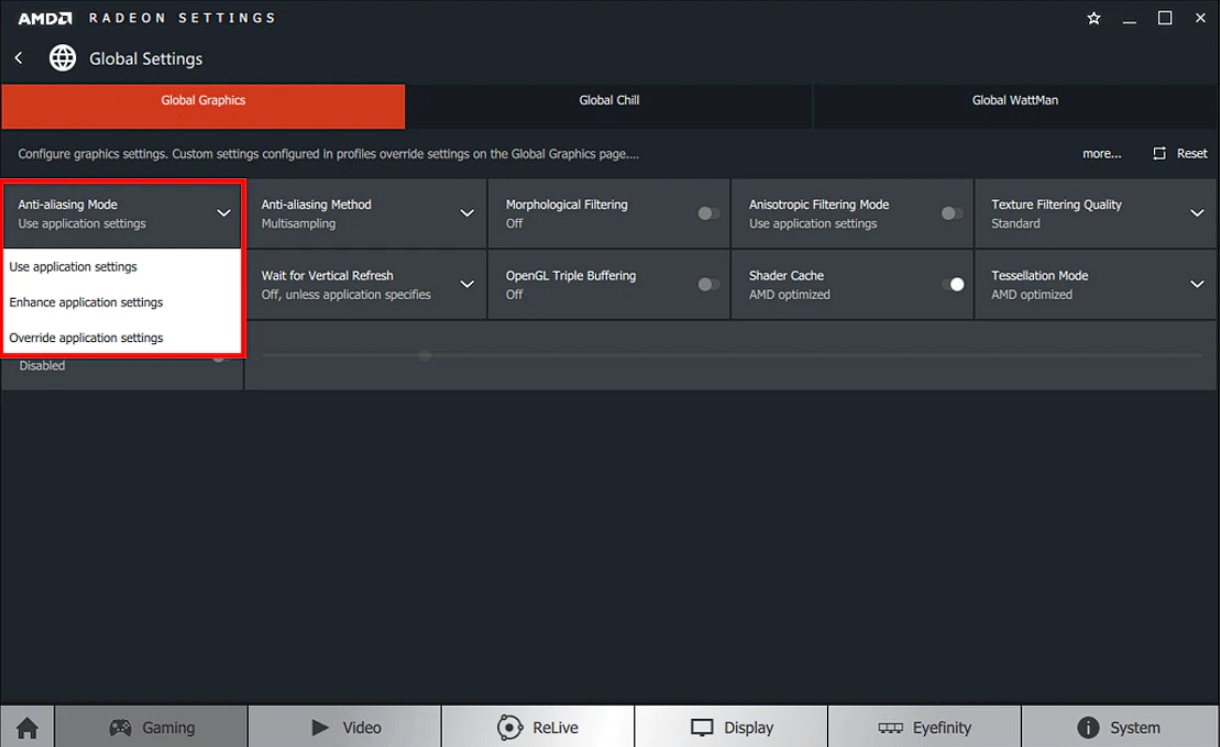
Selecting Anti-Aliasing Mode enables three options:
- Use Application Settings – Provides the 3D application with full control over the level of AA applied. Image quality is controlled via the 3D application graphics settings.
- Enhance Application Settings – Offers the flexibility of improving on existing AA used in the 3D application, by having the driver apply a second pass of AA.
- Override Application Settings – Allows Radeon Settings full control over the level of AA applied to the 3D application.
Selecting Override Application Settings enables different levels of AA to be applied to the 3D application.
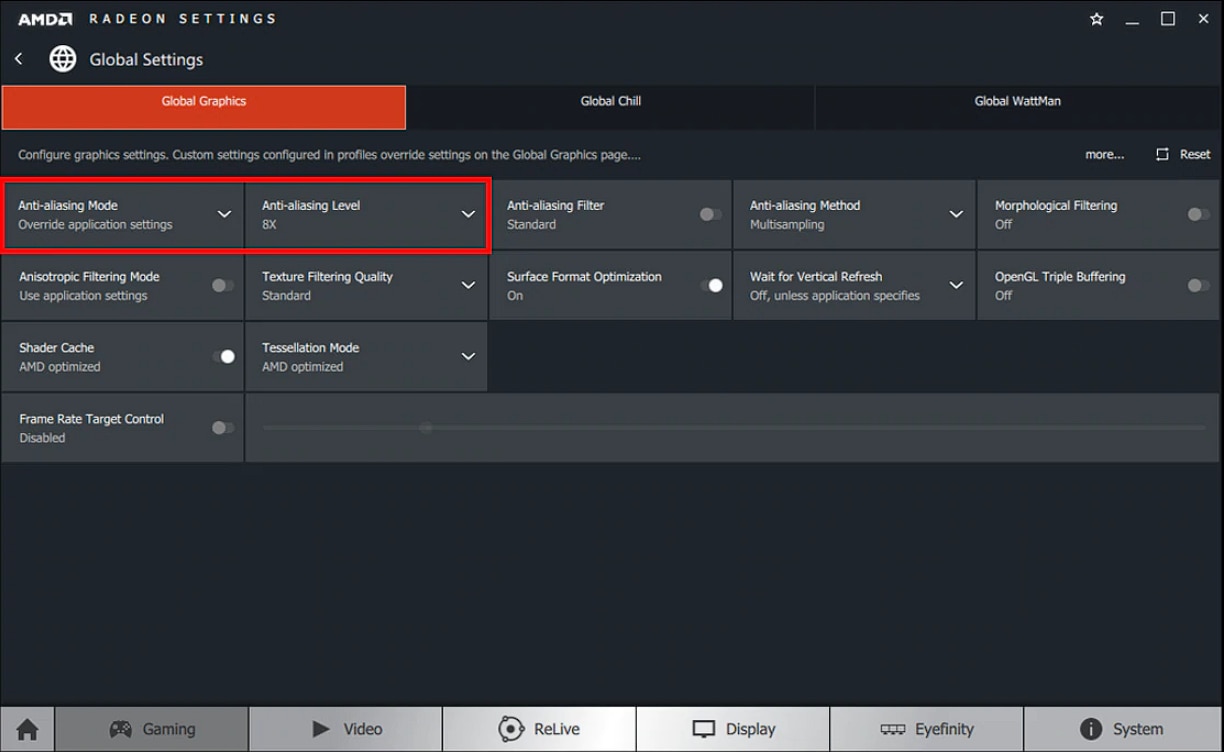
Anti-Aliasing Level can be set to x2, x4, or x8 and a higher number should improve image quality at expense of lower FPS.
Morphological Filtering
Morphological Filtering is a Shader based, post process Anti-Aliasing technique that can be used in combination with the three AA modes mentioned above.
Morphological Filtering can have a lower impact on FPS than other AA modes available within Radeon™ Settings, however in some situations it may introduce a subtle blur to the image.
In the example below, the image on the left has Morphological Filtering applied. The image on the right has no Morphological Filtering applied and has more jagged edges.

Morphological Filtering can be applied using Override or EnhanceApplication Settings and requires that the application is running in exclusive full screen mode.
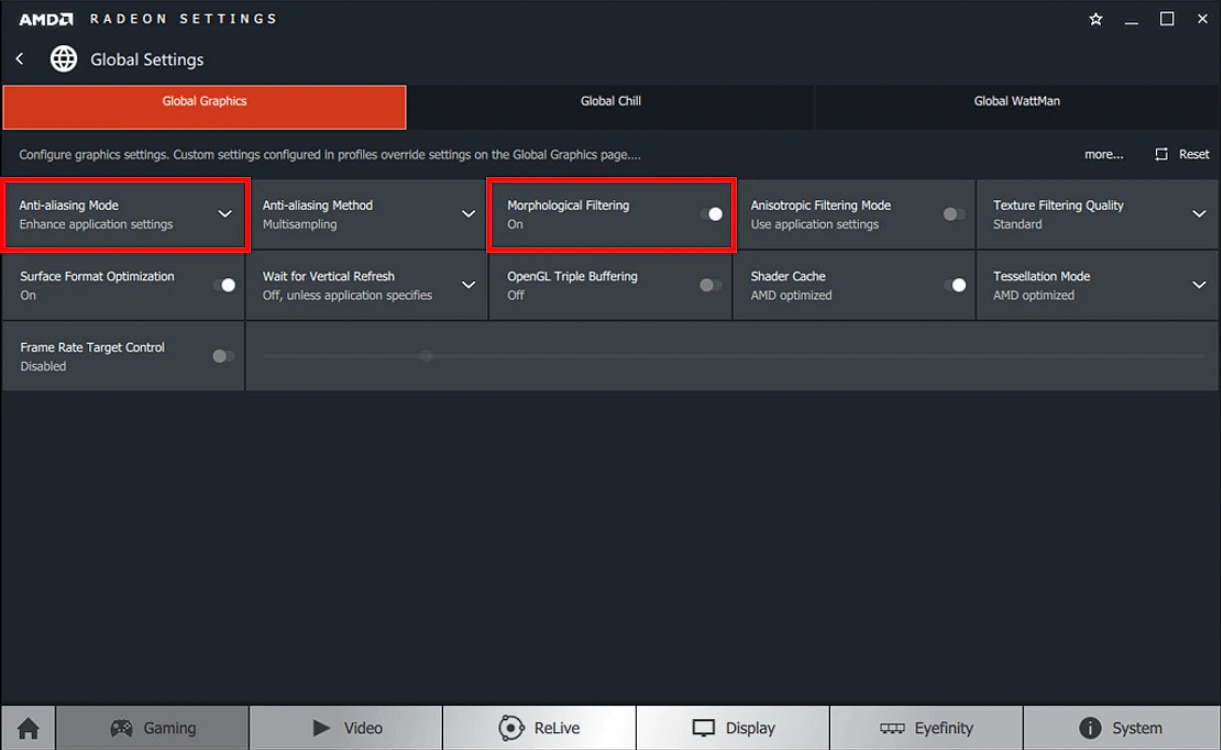
Morphological Filtering can be set to On or Off.
Anisotropic Filtering
Anisotropic Filtering can increase and sharpen the quality of textures on surfaces that appear far away or at odd angles, such as road surfaces or trees.
Anisotropic Filtering has a small performance cost (FPS) and can increase image quality in most 3D applications.
In the example below, the image on the left has Anisotropic Filtering applied, increasing the number of textures on the tree. The image on the right has no Anisotropic Filtering applied.
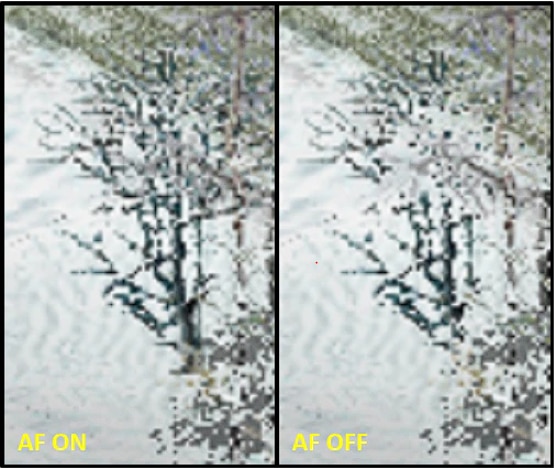
Anisotropic Filtering can be applied using Override Application Settings.
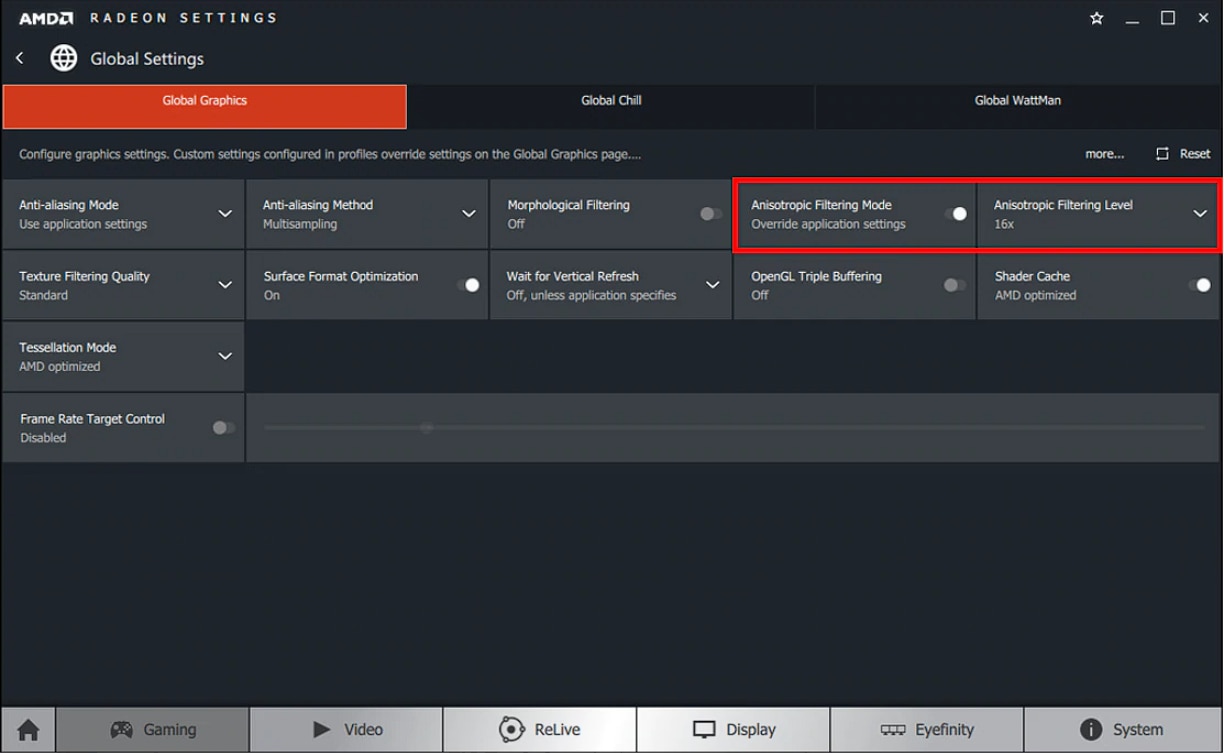
Anisotropic Filtering Level can be set to x2, x4, x8 or 16x and should improve image quality at expense of lower FPS.
Texture Filtering Quality
Texture Filtering Quality changes the quality of textures while running 3D applications.
Texture Filtering Quality has a small impact on performance and image quality, which makes the default setting of Standard the preferred option for the optimal gaming experience.

Shader Cache is set to AMD optimized by default and can be disabled globally by setting the feature to off.
Tessellation Mode
Tessellation Mode enhances the detail of objects by adjusting the number of polygons used for rendering.
Limiting the level of Tessellation can provide higher FPS in games that use high levels of tessellation.
In the example below, the image on the left has x64 Tessellation applied, increasing the detail of the bricks. The image on the right has no Tessellation applied and has less detail.

Tessellation Mode can be applied using Override Application Settings.
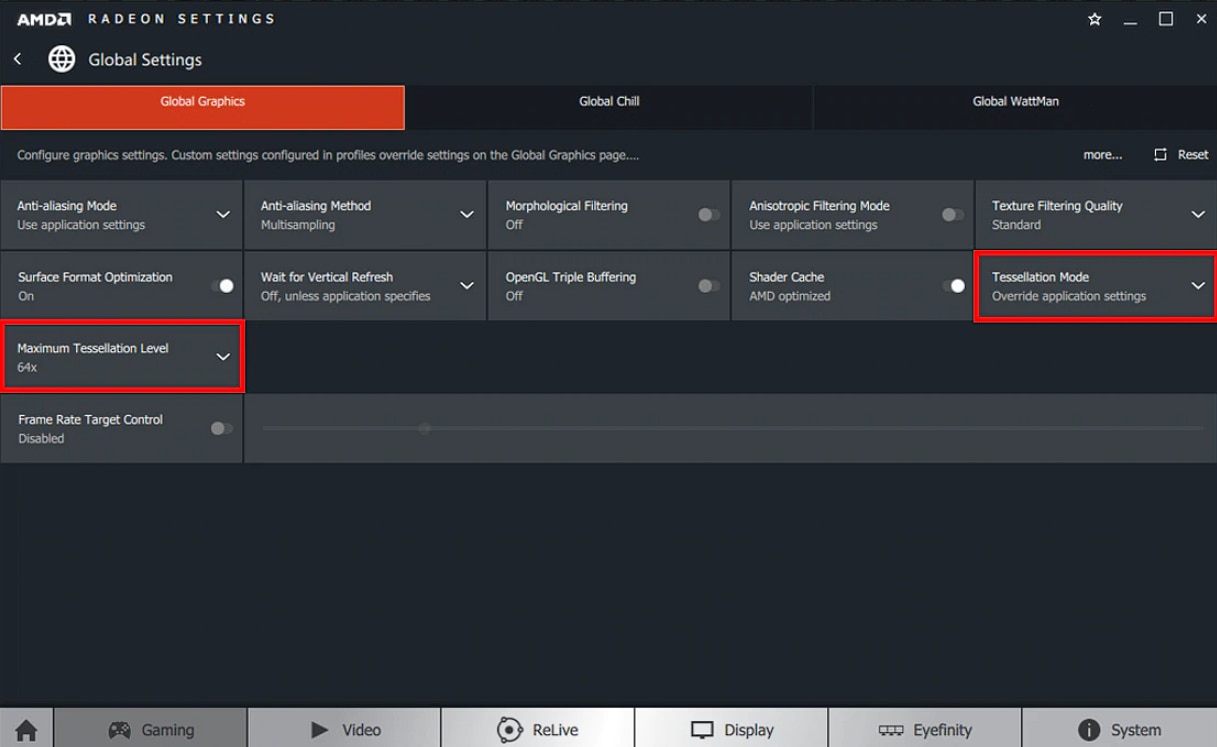
Maximum Tessellation Level can be set to x2, x4, x6, x8, x16, x32 or x64 and should improve image quality at expense of lower FPS.
Wait for Vertical Refresh
Vertical Refresh or VSync, synchronizes the application with the monitor frame rate with the objective of removing screen tearing.
Note! Wait for Vertical Refresh only works OpenGL 3D applications. When using other APIs such as DirectX® or Vulkan®, VSync is controlled via the 3D application graphics settings.

Wait for Vertical Refresh can be set to:
- Always Off
- Off, Unless Application Specifies
- On, Unless Application Specifies
- Always On
OpenGL Triple Buffering
When used in tandem with Wait for Vertical Refresh, OpenGL Triple Buffering can provide higher frame rates than with the default double buffering.
Note! OpenGL Triple Buffering requires Wait for Vertical Refresh to be set to Always On and applies only to OpenGL 3D applications.

OpenGL Triple Buffering can be set to ON or OFF.
Frame Rate Target Control
Frame Rate Target Control (FRTC) enables users to set a target maximum frame rate when running a 3D application in full screen mode; the benefit being that FRTC can reduce GPU power consumption (great for games running at frame rates much higher than the display refresh rate) and therefore reduce heat generation and fan speeds/noise on the graphics card.
FRTC is especially useful when rendering mostly static content on powerful hardware where framerates can often run needlessly into the hundreds of fps on game menus or splash screens.
If you have an AMD FreeSync™ compatible system, FRTC can ensure that you do not exceed the maximum FreeSync range of your display, resulting in a smooth, optimal gaming experience.
Note! Changes to the Frame rate target must be done outside of the game, i.e. exit the game completely, make your changes, and then start the game again.
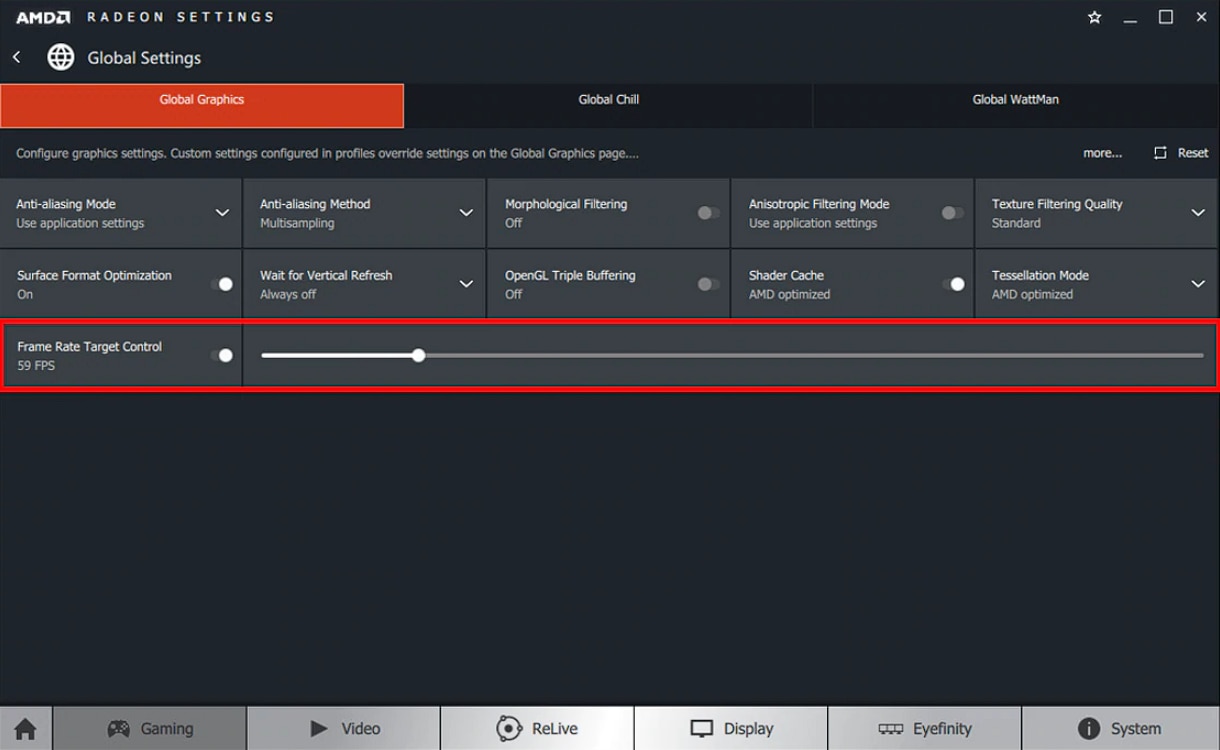
FRTC can be set to values between 30 and 200 FPS and works with DirectX® 9, 10 and 11 3D applications.
Click here to check if your graphics card is compatible with FRTC.
Restoring Default Settings
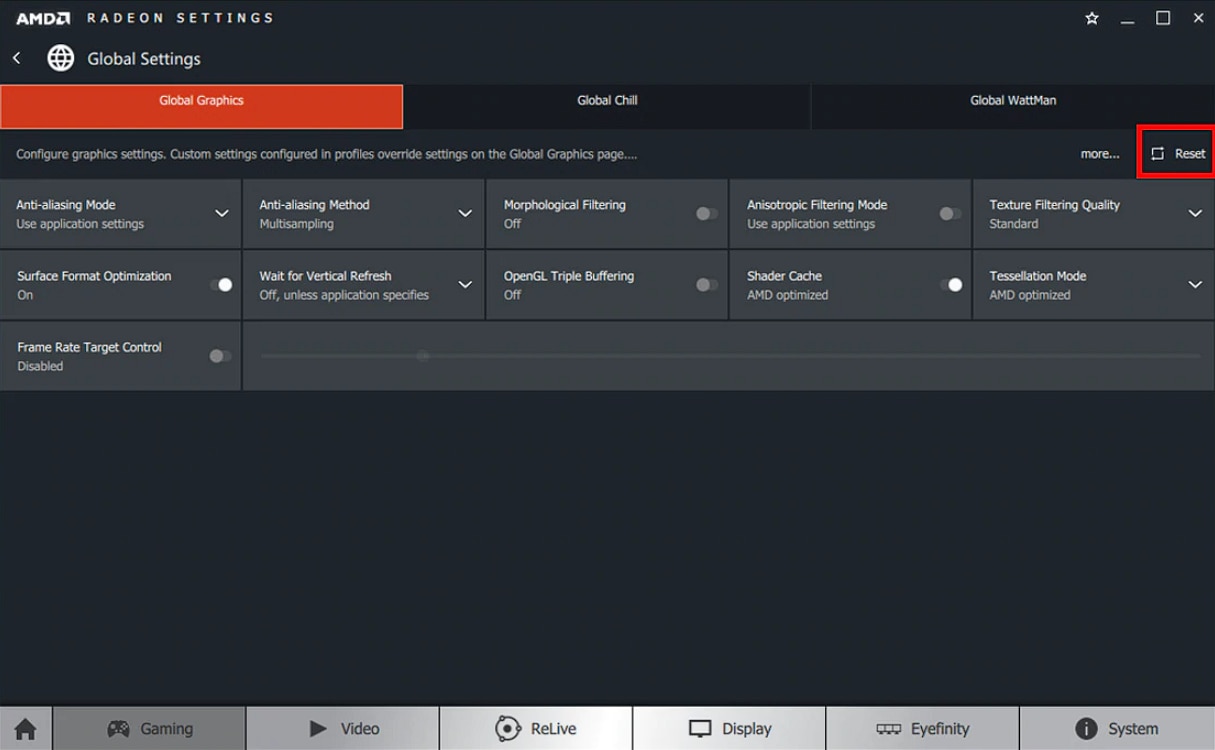
Finding the optimal balance of visual quality and performance may require many adjustments.
If you are not satisfied with results during gameplay, you can restore Global or individual Application Settings to default by clicking on the Reset option located in the upper right corner of the Global Graphics menu.
Find and select the application to add to Radeon Settings and click Open.
The application should now appear in the Gaming sections of Radeon Settings
Click on the application tile to customize its graphics settings.

Once the application profile is configured, the settings should apply to the application every time it is launched.