Another Generation of Leadership - AMD EPYC™ 9005 vs. Intel Xeon 6
May 15, 2025

Billions of people, leading Fortune 500 companies, and top-tier scientific research institutions around the world, rely on AMD technology every day to enhance how they live, work, and play. Last October, we introduced our 5th generation processors, featuring a range of industry-leading innovations. I'm excited to return with another blog focused on these processors. In my previous post (here), I compared our 5th generation processors to Intel’s latest at the time—their 5th generation. Now that Intel has launched its 6th generation processors and systems are widely available, I’d like to provide an updated competitive analysis, focusing on performance across key workloads.
Thanks to Our Partners
I’m incredibly grateful to our ecosystem partners, who have continued to collaborate closely with our engineers to deliver a wide range of datacenter solutions, including—but certainly not limited to—the following:
Alibaba, Altair, Anjuna, Ansys, AspenTech, Astera, Autodesk, Azure, Amazon, Broadcom, ByteDance, Cadence, Canonical, Casa Systems, CGG, Chaos Group, Cisco, Citrix, Cloudera, Cloudian, Cohesity, Convergent Science, Cornelis, Couchbase, Dassault Systèmes, Databricks, DataStax, Dell, Elastic, Emerson, Epic, Ericsson, ESI, Exasol, F5 Networks, Flow Science, Google, Halliburton, Hexagon, HPE, HuggingFace, Juniper Networks, Keysight, KIOXIA, Lenovo, MarkLogic, Marvell, Mavenir, MaxLinear, Microchip, Micron, Microsoft, MongoDB, Montage, NetScout, Neural Magic, Nokia, Nutanix, Nvidia, Oracle, Pivot3, Pixar, Quobyte, Radisys, Red Hat, RedisLabs, Rescale, Samsung, SAP, Sentieon, Shearwater, Siemens, SK Hynix, SLB, SnowFlake, Solidigm, Splunk, StorMagic, Supermicro, SUSE, Synamedia, Synopsys, Tencent, TigerGraph, Transwarp, VAST Data, Vertica, Viavi Solutions, VMware by Broadcom, Weka, Wind River, Western Digital, XConn and others.
We also collaborate with Apache Cassandra, Apache Spark, Apache Hadoop, Confidential Computing Consortium, CXL Consortium, Cloud Native Computing Foundation, FreeBSD Foundation, Linux Foundation, OpenAnolis Community, OpenCloudOS community, OpenEuler Community, and others.
Please visit the AMD Data Center Partner Ecosystem page to see the full list of AMD EPYC ecosystem partners.
About this blog
In this blog, I compare 5th Gen AMD EPYC processors to demonstrate our ongoing commitment to innovation and performance improvements across generations. The latest EPYC family delivers a wide spectrum of choices, featuring processors with 8 to 192 cores and TDPs ranging from 155W to 500W. I focus specifically on the 128-core and 192-core 5th Gen AMD EPYC models in comparison to Intel’s 6th Gen Xeon Scalable processor, codenamed Granite Rapids.
General Purpose Computing
The SPEC CPU® 2017 benchmark is a highly regarded, regulated, and audited industry standard for assessing compute-intensive workloads. It rigorously tests processors, memory subsystems, and compilers across a variety of systems, providing valuable insights into performance and efficiency. This benchmark serves as a critical tool for evaluating the capabilities of modern computing architectures. It includes 43 benchmarks divided into four suites. This blog focuses on SPECrate® 2017 Integer and SPECrate® 2017 Floating Point—perhaps two of the most foundational points of comparison that customers request.
Figure 1 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECrate® 2017_int_base uplifts of ~1.13x and ~1.29x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.1
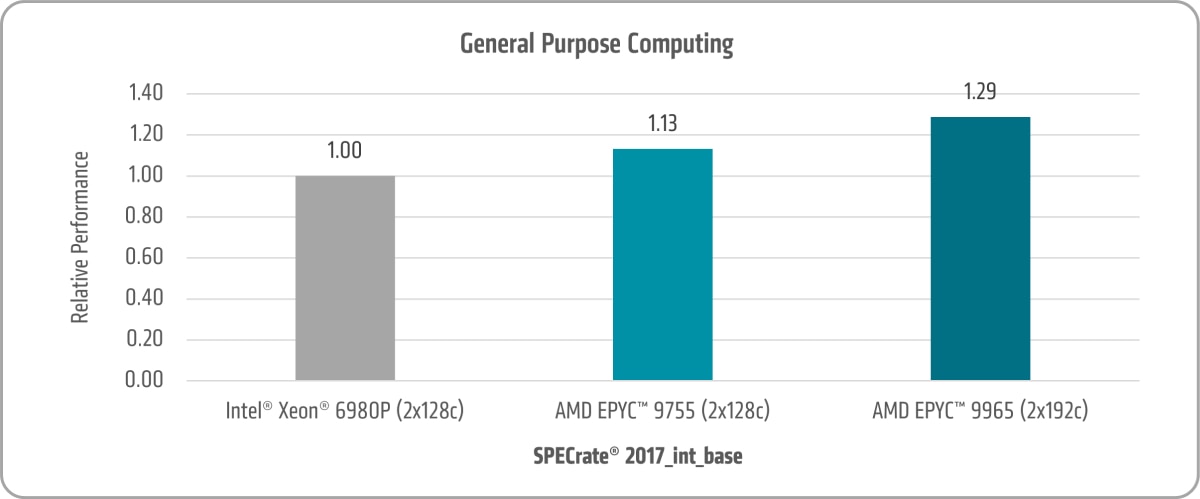
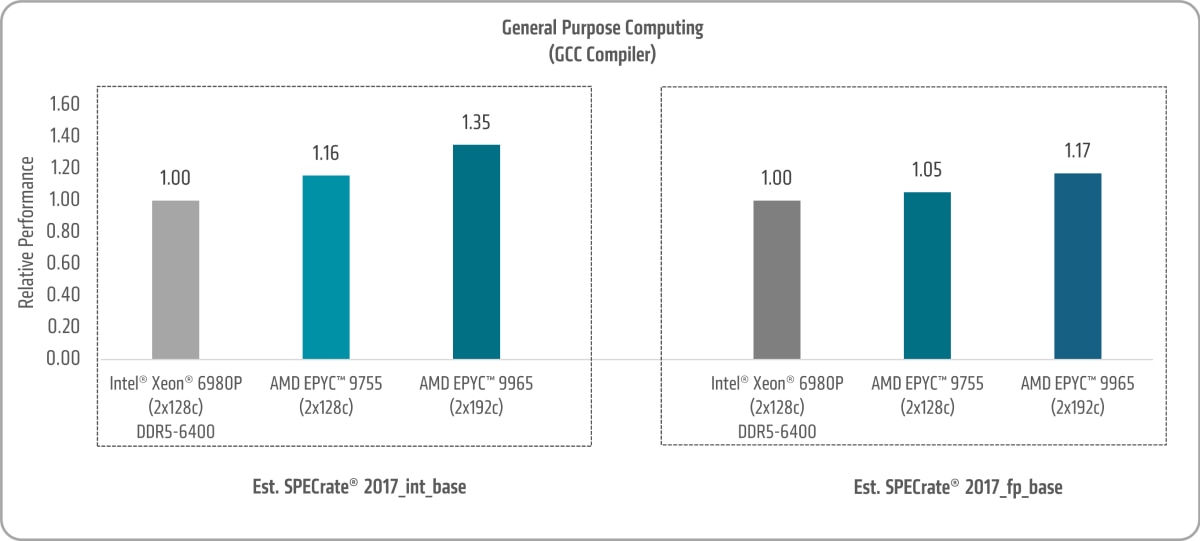
Figure 2 illustrates that with GCC compiler:
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECrate® 2017_int_base uplifts of ~1.16x and ~1.35x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.2
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECrate® 2017_fp_base uplifts of ~1.05x and ~1.17x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.5
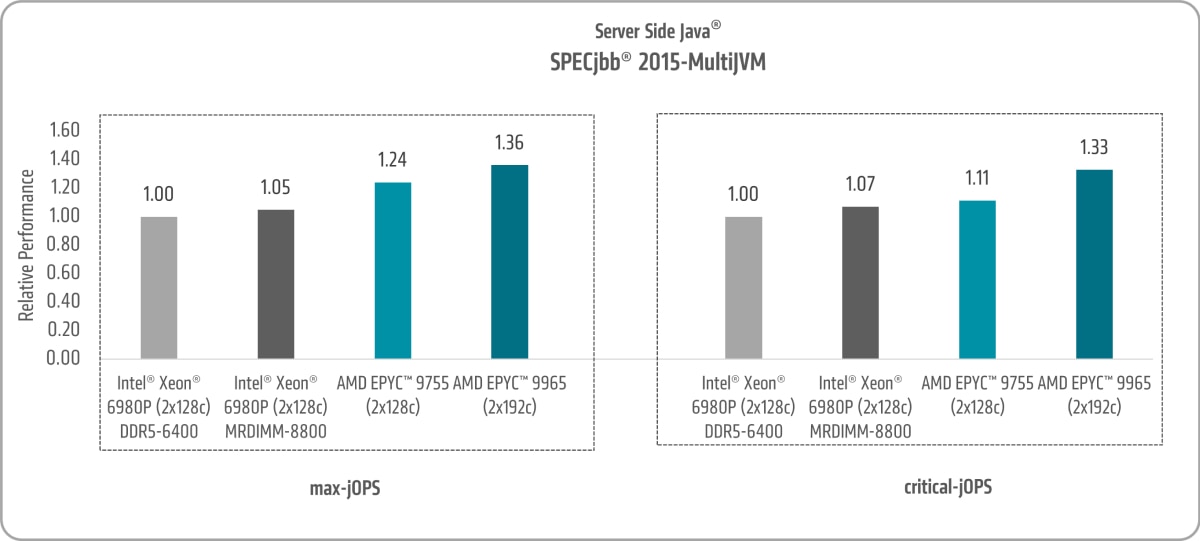
Server Side Java
Java® is a versatile and powerful programming language known for its portability, allowing developers to create applications that run seamlessly across different platforms. The SPECjbb® 2015 benchmark assesses the performance of server-side Java applications by simulating a corporate IT environment that handles a mix of point-of-sale requests, online transactions, and data-mining tasks. Its relevance extends to Java Virtual Machine (JVM) vendors, hardware manufacturers, Java application developers, researchers, commercial and end users, and academia.
The SPECjbb® 2015 benchmark includes two key metrics: max-jOPS and critical-jOPS. Max-jOPS measures the highest throughput for Java e-commerce transactions, reflecting the system's maximum capacity. In contrast, critical-jOPS indicates the throughput that meets the p99 response time criteria, representing the typical operational range for latency-sensitive Java e-commerce applications.
Figure 3 shows both:
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECjbb® 2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS uplifts of ~1.24x and ~1.36x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.3
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECjbb® 2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS uplifts of ~1.11x and ~1.33x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.4
Energy Efficiency
Efficient power consumption is crucial for today's data centers, as it helps lower cooling needs, cut utility costs, and support sustainability objectives. The SPEC CPU®2017 Integer Rate Energy metric builds on the well-known SPEC CPU®2017 Integer Rate benchmark by adding energy efficiency measures. This metric assesses both performance and power usage, positioning itself as the industry standard for evaluating efficiency.
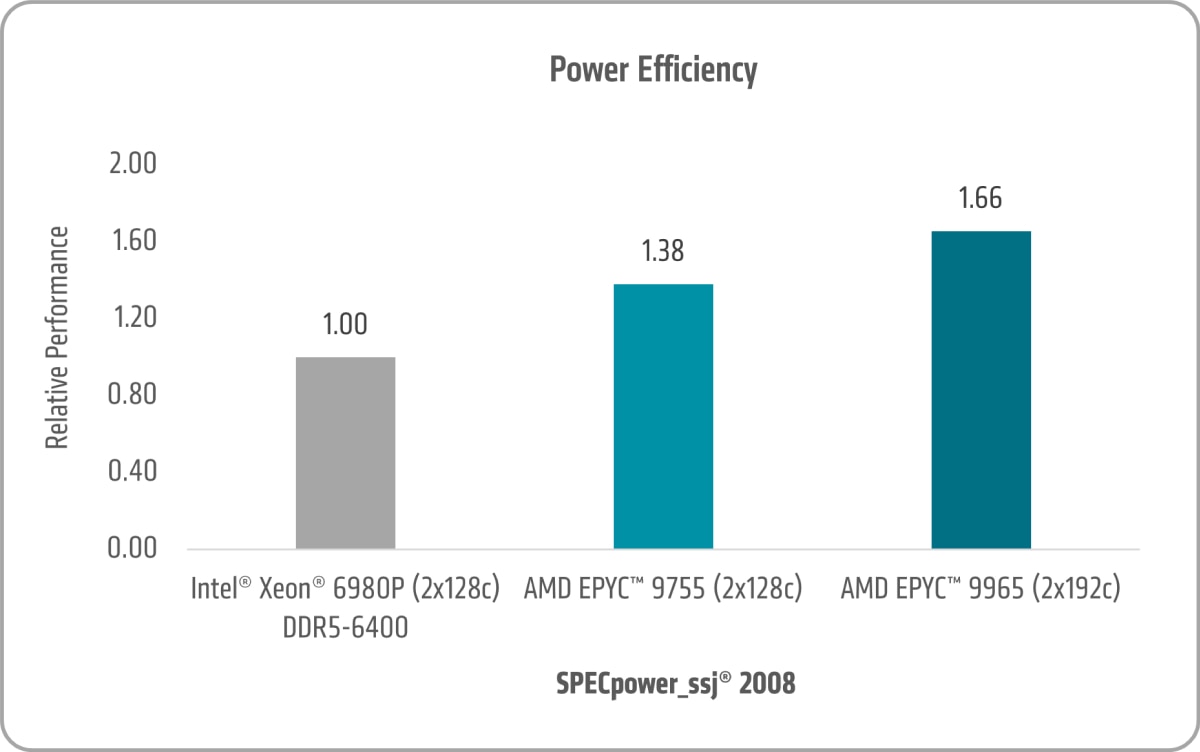
Figure 4 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 SPECpower_ssj® 2008 uplifts of ~1.38x and ~1.66x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.7
Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS)
MySQL™ is one of the most widely used open-source database management systems globally. It is commonly employed in enterprises and cloud-native environments for both decision support and transaction processing systems. AMD used TPROC-H to evaluate the performance of decision support systems and TPROC-C for transaction processing systems.
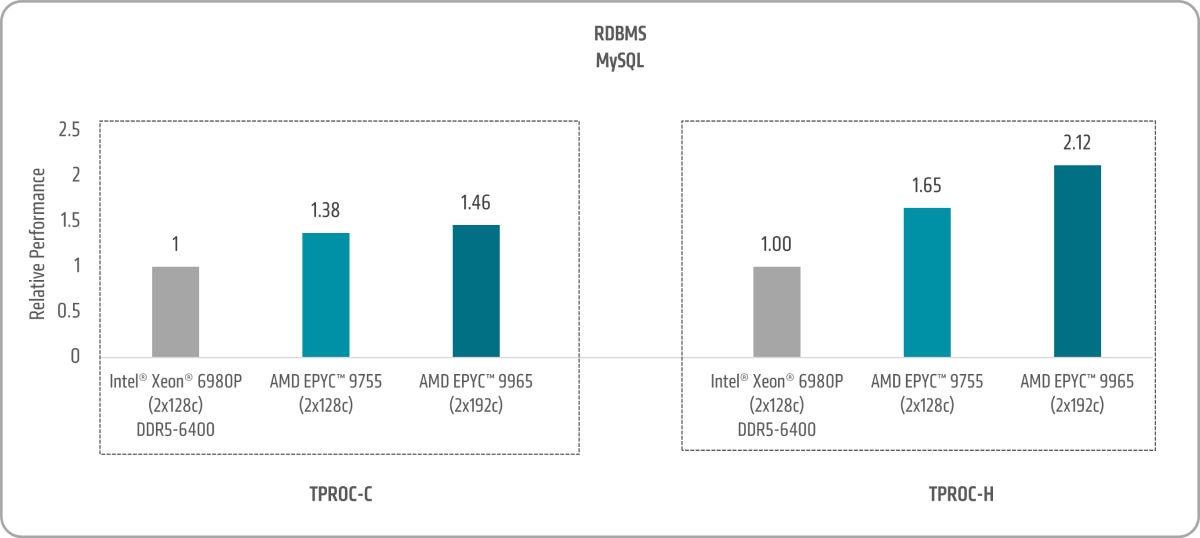
Figure 5 shows both:
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 MySQL TPROC-C uplifts of ~1.38x and ~1.46x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.8
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 MySQL TPROC-H uplifts of ~1.65x and ~2.12x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.9
The HammerDB TPROC-C workload is an open-source workload derived from TPC-Benchmark™ Standard, and as such is not comparable to published TPC-C™ results, as the results do not comply with the TPC-C Benchmark Standard. Likewise, The HammerDB TPROC-H workload is an open-source workload derived from TPC-Benchmark™ Standard, and as such is not comparable to published TPC-H™ results, as the results do not comply with the TPC-H Benchmark Standard.
Web Server
NGINX™ is a popular web server known for its flexibility to act as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy, and HTTP cache. It's designed to efficiently handle client requests and deliver web content. NGINX can operate as a standalone web server or boost performance and security by serving as a reverse proxy for other servers. AMD used the popular WRK tool to evaluate performance by generating significant HTTP loads during benchmark testing.
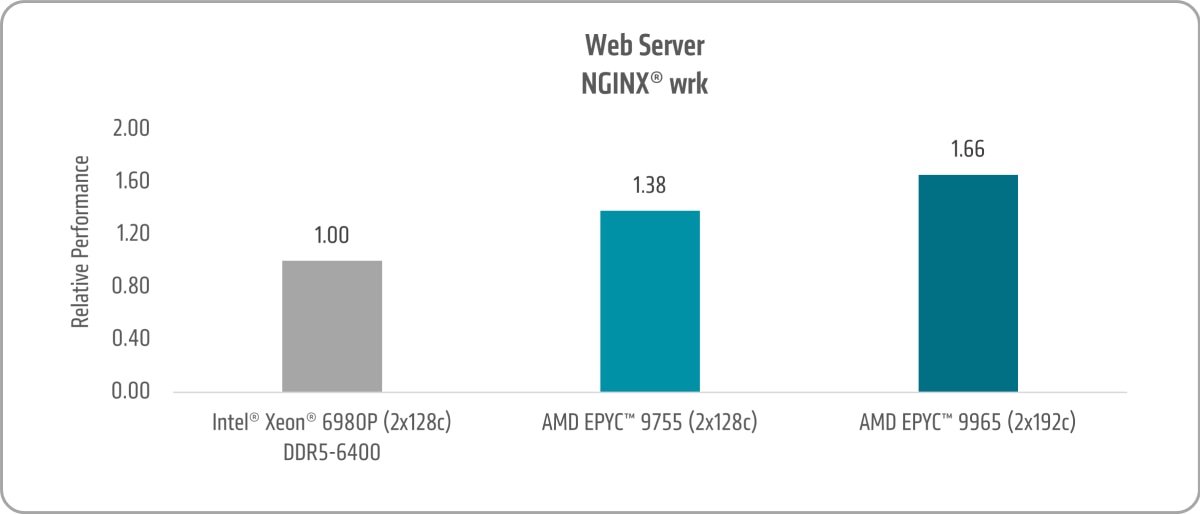
Figure 6 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 NGINX® WRK uplifts of ~1.38x and ~1.66x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.10
In-Memory Analytics
Redis™ is a popular in-memory data store that works as a key-value database, cache, and message broker, with optional durability features. It's great for cloud environments and supports functions like streaming, microservices, and data analytics, helping users to be more productive. Redis can handle various data types, including strings, lists, maps, and more. Its in-memory design provides excellent performance.
AMD used a tool called redis-Benchmark to measure how well Redis performs. This tool simulates multiple clients connecting to the server and measures how long it takes to complete requests. The results show the average number of requests your Redis server can handle per second.
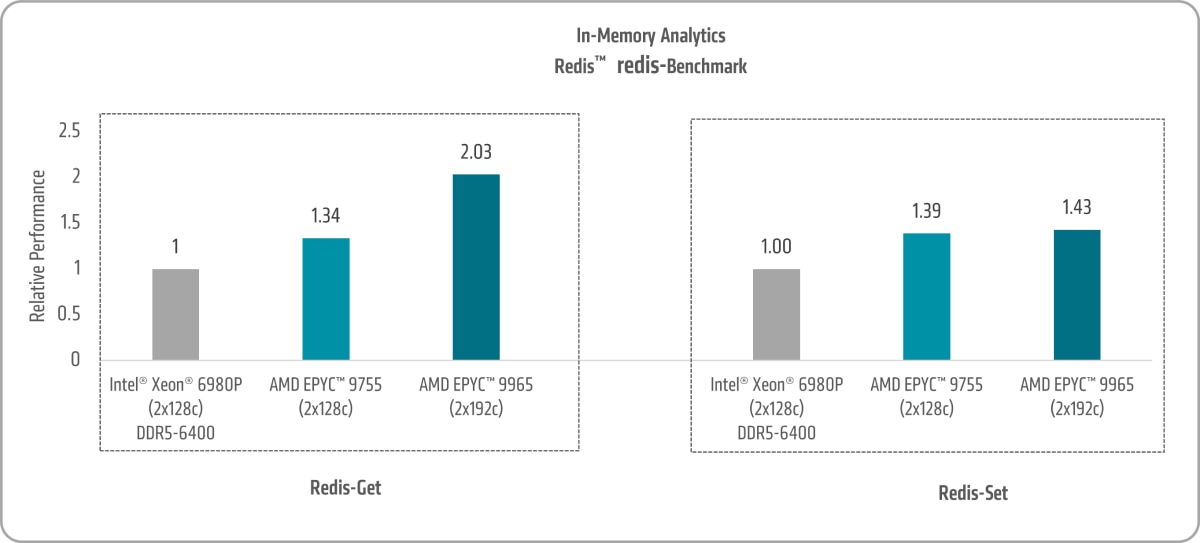
Figure 7 shows both
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 Redis-Get uplifts of ~1.34x and ~2.03x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.11
- 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 Redis-Set uplifts of ~1.39x and ~1.43x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.12
Media Processing
FFmpeg is a powerful, free, and open-source software project that offers a comprehensive set of libraries, codecs, and tools for handling video, audio, and multimedia files and streams. The core FFmpeg program is designed for command-line processing, making it a popular choice for tasks such as encoding, transcoding, editing, video scaling, post-production, and ensuring compliance with multimedia standards.
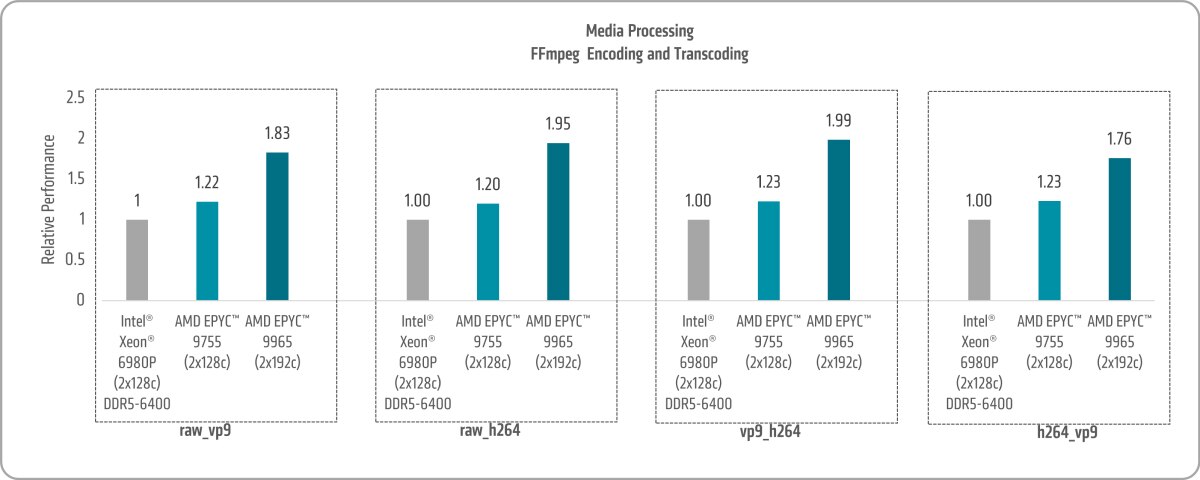
As illustrated in Figure 8, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and 6th Gen AMD EPYC 9965 achieve FFmpeg performance gains of up to 1.23x and 1.99x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.13
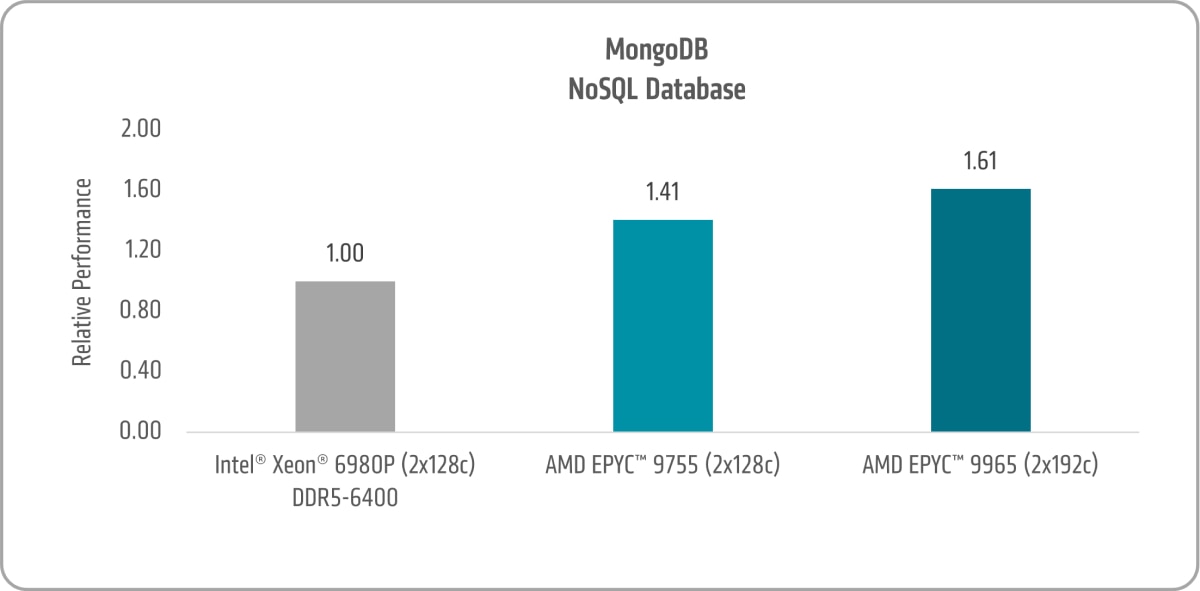
NoSQL Database
MongoDB is an open-source, document-based NoSQL database designed to handle large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently. It is widely used in modern applications such as social media platforms, content management systems, mobile apps, and e-commerce sites, where flexibility, scalability, and performance are essential.
For competitive analysis, we utilized the popular Yahoo! Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB), an open-source framework that evaluates and compares the performance of various cloud databases and storage systems under different workloads.
As illustrated in Figure 9, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 achieve MongoDB® database performance gains of 1.41x and 1.61x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.27
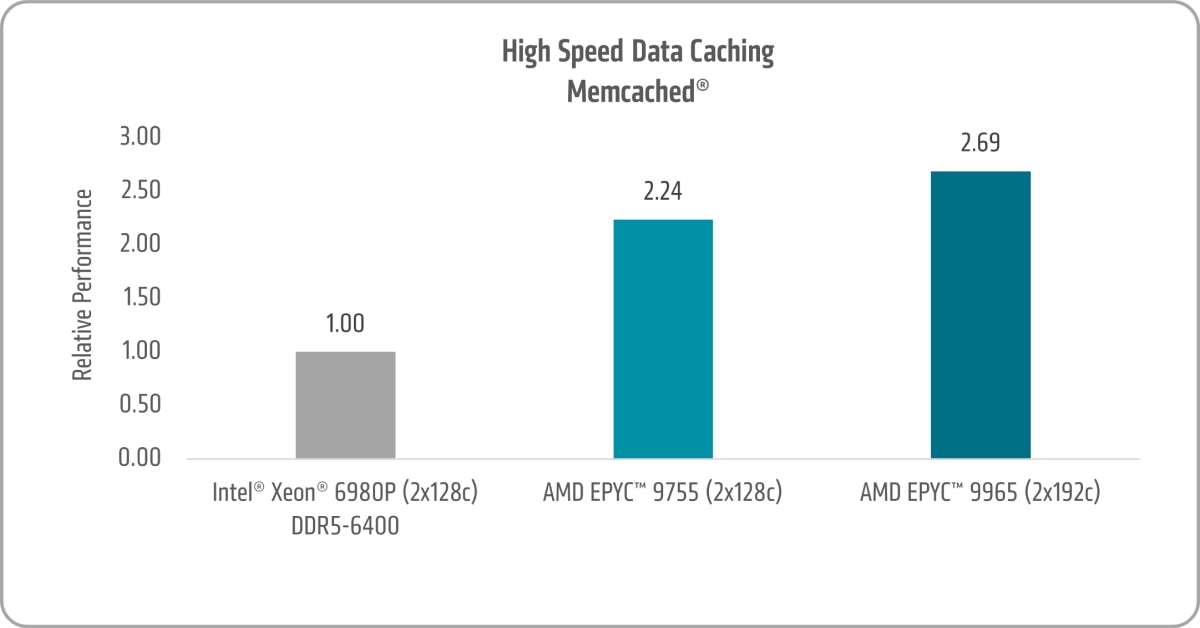
Memcached® High Speed Data Caching
Memcached™ is a high-performance, distributed, in-memory caching system that stores key-value pairs for small pieces of arbitrary data, such as strings and objects, sourced from database calls, APIs, or rendered pages. It is widely used in cloud environments for its ability to quickly serve cached items while enabling easy scaling and cost-effectiveness under heavy loads. Memcached is often employed to cache database query results, session data, web pages, APIs, and objects like images, files, and metadata. Built for simplicity and efficiency, it supports rapid development and deployment to tackle the challenges of large data caches.
To assess its performance, AMD utilized the Memtier Benchmark, which measures throughput and latency across different configurations.
As illustrated in Figure 10, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 achieve Memcached® performance gains of up to 2.24x and 2.69x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.26
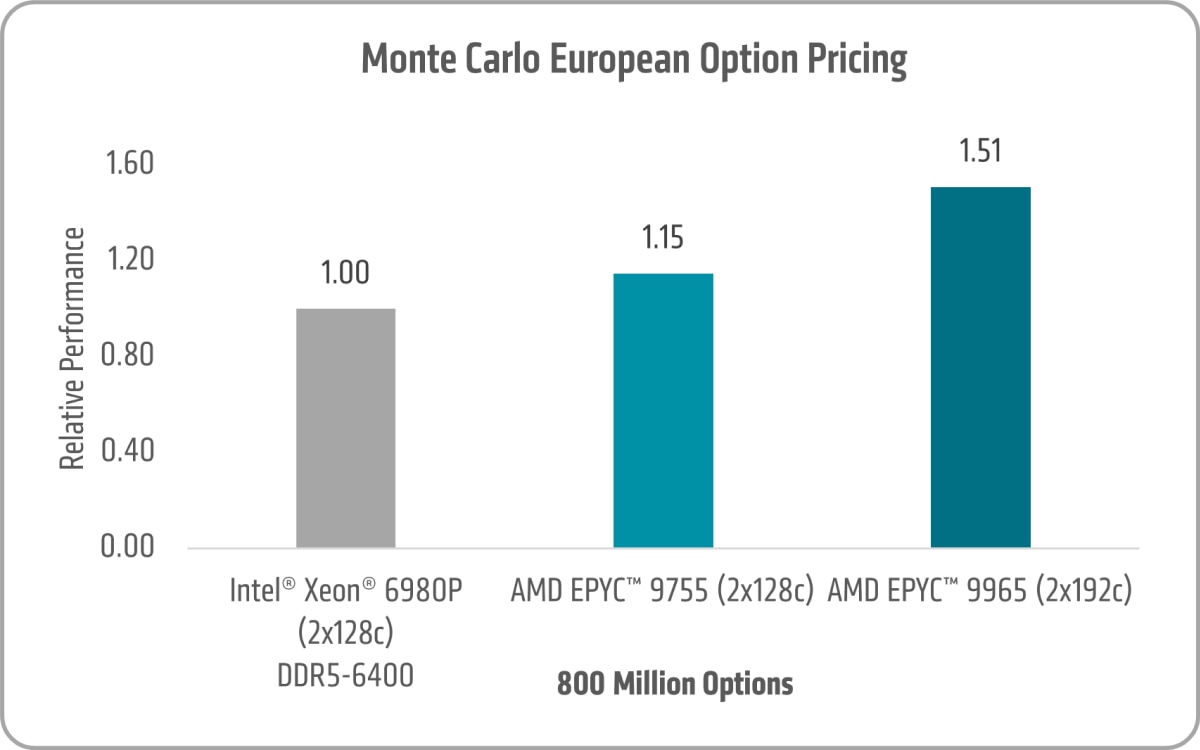
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is a statistical technique that uses random sampling to model and analyze complex systems or processes, helping to estimate the likelihood of different outcomes and assess uncertainty in decision-making.
As illustrated in Figure 11, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and 6th Gen AMD EPYC 9965 achieve performance gains of 1.15x and 1.51x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.28
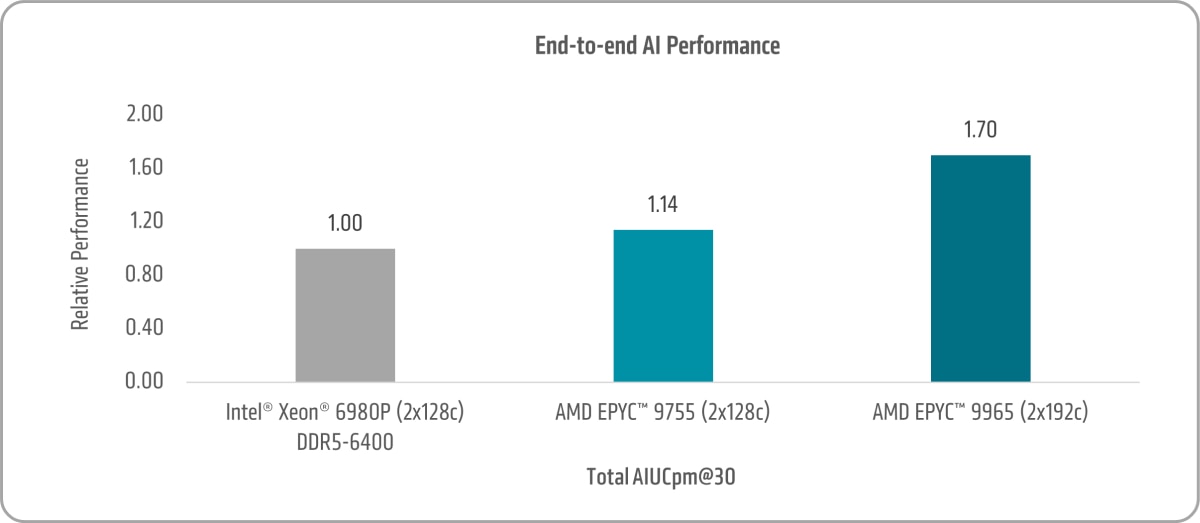
End-to-end AI Performance
The TPCx-AI benchmark, developed by the Transaction Processing Performance Council (TPC), is a thorough, end-to-end workload designed to assess the performance of systems managing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) pipelines. It simulates real-world AI applications and offers a standardized metric to compare hardware and software solutions across various environments.
For competitive comparisons, we used a workload derived from the TPCx-AI benchmark (with multiple users running simultaneously). However, since these results do not comply with the TPCx-AI submission guidelines, they cannot be directly compared to published results.
As illustrated in Figure 12, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 achieve TPCx-AI@SF30 performance gains of 1.14x and 1.70x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.24
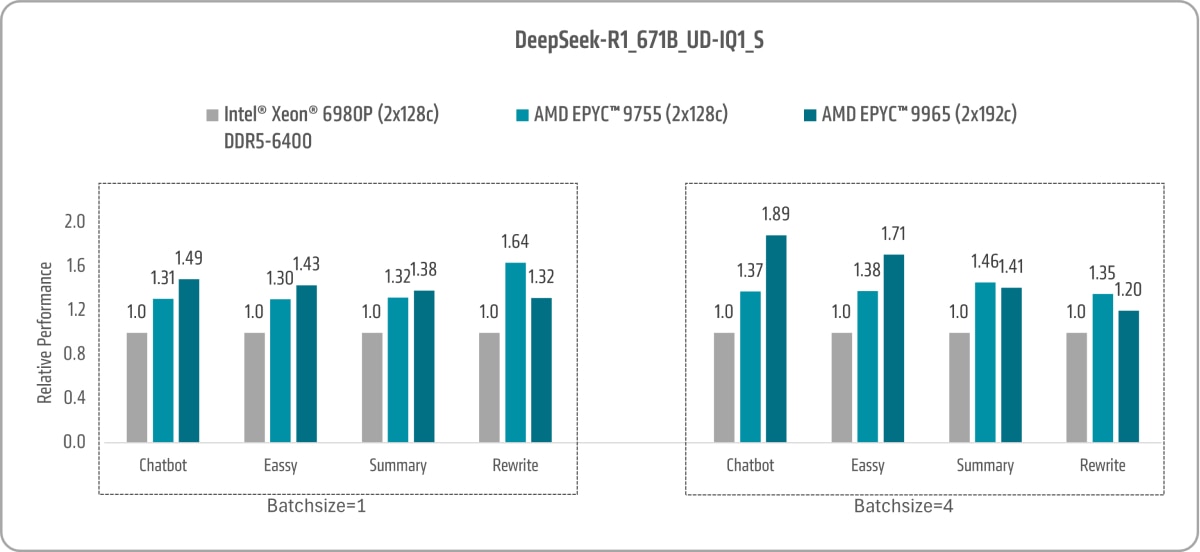
DeepSeek
DeepSeek is an advanced AI-powered search and discovery platform that leverages deep learning technologies to improve data retrieval and knowledge exploration. Its flagship model, R1, released in 2025, is designed for tasks such as logical inference and real-time problem-solving.
For performance comparison, we ran a virtual machine with 16 cores, utilizing the DeepSeek UD-IQ1-S model, which features a total of 671B parameters, with 37B parameters activated, using Llama.cpp.
As shown in Figure 13, the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 achieved DeepSeek performance gains of up to 1.64x and 1.89x, respectively, when compared to the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P.25
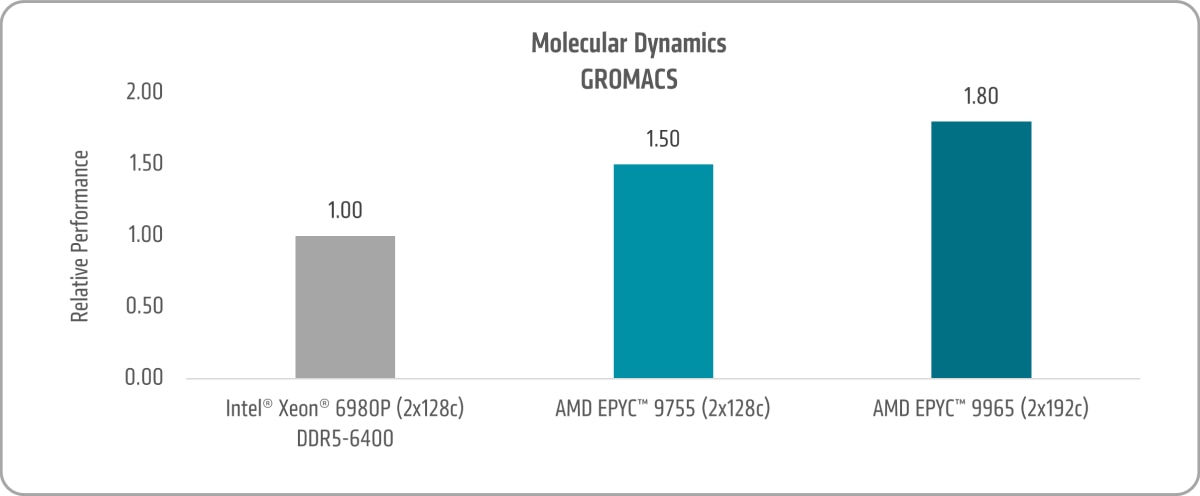
Molecular Dynamics
GROMACS is a molecular dynamics application that simulates Newtonian motion for systems ranging from hundreds to millions of particles.
Figure 15 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 GROMACS uplifts of ~1.5x and ~1.8x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.14,15
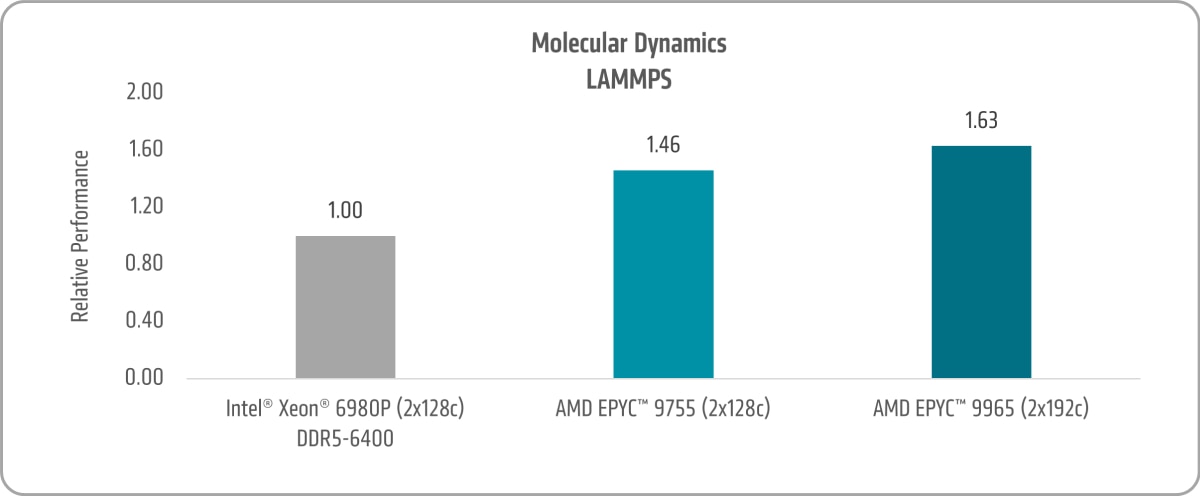
LAMMPS is a classical molecular dynamics application with a focus on materials modeling. LAMMPS has uses for both solid state materials and biosciences.
Figure 16 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 LAMMPS uplifts of ~1.46x and ~1.63x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.16,17
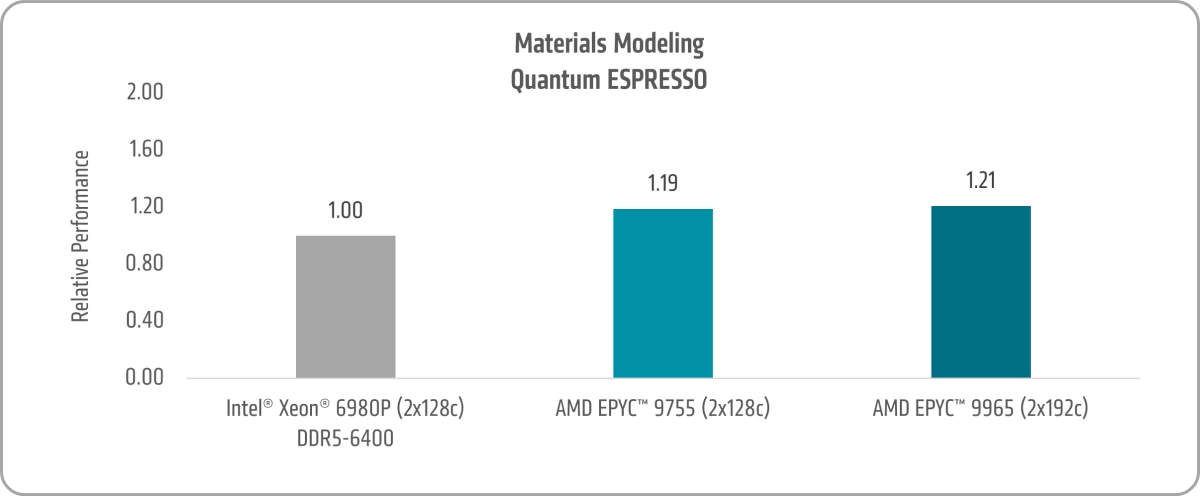
Materials Modeling
Quantum ESPRESSO is an open-source suite for nanoscale electronic-structure calculations and materials modeling using density-functional theory, plane waves, and pseudopotentials. The Quantum ESPRESSO 7.0 ausurf benchmark was used to compare system performance.
Figure 18 shows the 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9755 and AMD EPYC 9965 Quantum ESPRESSO uplifts of ~1.19x and ~1.21x versus the 6th Gen Intel Xeon 6980P, respectively.20,21
Wrapping Up
The 5th Generation AMD EPYC processors mark a major advancement in server technology, building on AMD's leadership in x86 architecture with higher core counts, advanced multi-threading, superior performance, and exceptional energy efficiency. Designed to meet the rapidly growing demands for performance, capacity, and efficiency in modern data centers, the AMD EPYC architecture provides outstanding value across a wide range of applications, including critical enterprise and cloud-native workloads. These processors feature a state-of-the-art design with increased core counts, improved instructions per cycle (IPC), and enhanced memory and I/O bandwidth, all while integrating cutting-edge confidential computing technologies. This innovative processor sets a new benchmark in server performance, made possible through the strong collaboration with our ecosystem partners.
Raghu Nambiar is a Corporate Vice President of Data Center Ecosystems and Solutions for AMD. His postings are his own opinions and may not represent AMD’s positions, strategies or opinions. Links to third party sites are provided for convenience and unless explicitly stated, AMD is not responsible for the contents of such linked sites and no endorsement is implied.
- 9xx5-128A: SPECrate®2017_int_base comparison based on published scores from www.spec.org as of 5/9/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (3230 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, $14,813 CPU $), 6.460 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU W, 0.218 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU $, https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2025q2/cpu2017-20250324-47086.html ) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (2840 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, $12,984 CPU $), 5.680 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU W, 0.219 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU $, https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2025q2/cpu2017-20250324-47223.html ) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (2510 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, $12,460 CPU $) 5.020 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU W, 0.201 SPECrate®2017_int_base/CPU $, https://www.spec.org/cpu2017/results/res2025q2/cpu2017-20250324-47099.html) SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECrate® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information. Intel CPU TDP and prices at https://ark.intel.com/ as of 4/17/2025.
- 9xx5-129: SPECrate®2017_int_base with GCC13 comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 4/1/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (est, 2160 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (est. 1850 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (est. 1600 SPECrate®2017_int_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP6 kernel 6.4.0-150600.23.33-default, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) The same Intel Xeon 6980P with 1.5TB 24x64GB MRDIMM at 8800MT/s, 1650 SPECrate®2017_int_base SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECrate® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information. Intel CPU TDP at https://ark.intel.com/ as of 4/17/2025
- 9xx5-130: SPECjbb® 2015-MultiJVM Max-jOPS comparison based on published scores from www.spec.org as of 4/17/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (1385555 SPECjbb® 2015-MultiJVM Max-jOPS, 714303 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 384 Total Cores, https://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q2/jbb2015-20250319-01562.html ) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (1262654 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS, 609560 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, https://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q2/jbb2015-20250319-01551.html 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (1066630 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS, 694290 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, MRDIMM at 8800 MT/s, http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q1/jbb2015-20241211-01502.html ) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (1017589 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS, 656307 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, DDR5-6400, http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q2/jbb2015-20250319-01553.html ) SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECjbb® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- 9xx5-131: SPECjbb® 2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS comparison based on published scores from www.spec.org as of 4/17/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (1078890 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS,1015843 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 384 Total Cores, http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q2/jbb2015-20250319-01561.html) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (889032 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS, 851468 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2024q4/jbb2015-20240918-01395.html) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (940159 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS, 818605 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, MRDIMM AT 8800 MT/S , http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q1/jbb2015-20241211-01505.html) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (883439 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM max-jOPS 764407 SPECjbb®2015-MultiJVM critical-jOPS, 256 Total Cores, DDR5-6400, http://www.spec.org/jbb2015/results/res2025q2/jbb2015-20250319-01552.html) SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECjbb® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- 9xx5-132: SPECrate®2017_fp_base with GCC13 comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 4/1/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (est, 1570 SPECrate®2017_fp_base, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic, SMT=OFF, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (est. 1410 SPECrate®2017_fp_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic, SMT=ON determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (est. 1340 SPECrate®2017_fp_base, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP6 kernel 6.4.0-150600.23.33-default, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) The same Intel Xeon 6980P with 1.5TB 24x64GB MRDIMM at 8800MT/s, 1490 SPECrate®2017_fp_base SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECrate® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information. Intel CPU TDP at https://ark.intel.com/ as of 4/17/2025
- 9xx5-133: SPECpower_ssj® 2008 comparison based on published scores from www.spec.org as of 4/17/2025. 1P AMD EPYC 9965 (36151 ssj_ops/watt, 192 Total Cores, http://www.spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2025q2/power_ssj2008-20250318-01509.html) 1P AMD EPYC 9755 (31874 ssj_ops/watt, 128 Total Cores, http://www.spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2024q4/power_ssj2008-20240923-01453.html) 1P Intel Xeon 6980P (20102 ssj_ops/watt, 128 Total Cores, https://www.spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2025q1/power_ssj2008-20241216-01477.html) SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECpower® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- 9xx5-134: SPECpower_ssj® 2008 comparison based on published scores from www.spec.org as of 4/30/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (35920 ssj_ops/watt, 384 Total Cores, https://spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2024q4/power_ssj2008-20241007-01464.html) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (29950 ssj_ops/watt, 256 Total Cores, https://spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2024q4/power_ssj2008-20240924-01460.html) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (21679 ssj_ops/watt, 256 Total Cores, https://spec.org/power_ssj2008/results/res2025q2/power_ssj2008-20250324-01511.html) SPEC®, SPEC CPU®, and SPECpower® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- 9xx5-135: MySQL TPROC-C workload (RDBMS) estimate based on internal AMD measurements as of 04/01/2025. The HammerDB TPROC-C workload is an open-source workload derived from TPC-Benchmark™ Standard, and as such is not comparable to published TPC-C™ results, as the results do not comply with the TPC-C Benchmark Standard. Workload configs: MySQL 8.0.41, 8 core nodes (Multi-SUT), HammerDB-4.4, duration 5min, 32 v users, warehouses 128, aggregate Orders Per Minute (OPM) 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (29,543,436 TPM, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (27,847,175 TPM, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (20,252,274 TPM, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings. TPC, TPC Benchmark, and TPC-C are trademarks of the Transaction Processing Performance Council.
- 9xx5-136: MySQL TPROC-H workload (RDBMS) estimate based on internal AMD measurements as of 04/01/2025. The HammerDB TPROC-H workload is an open-source workload derived from TPC-Benchmark™ Standard, and as such is not comparable to published TPC-H™ results, as the results do not comply with the TPC-H Benchmark Standard. Workload configs: MySQL 8.0.41, 8 core nodes (Multi-SUT), HammerDB-4.4, Scale Factor 30, aggregate Queries per Hour (QPH) 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (217,737 QPH, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference System, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (169,383 QPH, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference System, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (102,692 QphH, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings. TPC, TPC Benchmark, and TPC-H are trademarks of the Transaction Processing Performance Council.
- 9xx5-137: NGINX™ WRK comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (46,429,262 req/s, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (44,492,096 req/s, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD Reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (23,135,112 req/s, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-138: Redis™ GET comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. Workload configs: Redis 7.4.0, 4 core nodes (Multi-SUT), data size 1000, pipelinerequests=10 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (128,996,111 rps, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (84,839,654 rps, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (63,482,189 rps, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-139: Redis™ SET comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. Workload configs: Redis 7.4.0, 4 core nodes (Multi-SUT), data size 1000, pipelinerequests=10 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (71,633,562 rps, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (69,563,201 rps, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (50,138,725 rps, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-140: FFmpeg comparison based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. FFMPEG 6.1.1, 1 instance/thread, video source: ducks take off, 302 frames (Raw to vp9, Raw to h264, vp9 to h264, h264 to vp9) , frames per hour (fph) 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (16,382,980 fph, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (10,136,013 fph, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (8,239,577 fph, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) raw_vp9 raw_h264 vp9_h264 h264_vp9 6980P 1 1 1 1 9755 1.22 1.2 1.23 1.23 9965 1.83 1.95 1.99 1.76 Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-141: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (ns/day) of this benchmark for a 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source GROMACS 2023.1. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * gmx_water1536K_PME: ~1.50x * benchPEP: ~1.50x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: TVOT1003E BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-142: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (ns/day) of this benchmark for a 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source GROMACS 2023.1. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * gmx_water1536K_PME: ~1.76x * benchPEP: ~1.83x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 (384 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 3.84 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: RVOT1000C BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-143: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Number of Atoms) of this benchmark for a 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source lammps 20220623. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * lammps_HECBioSim_1400k: ~1.46x * lammps_HECBioSim_20k: ~1.52x * lammps_HECBioSim_3000k: ~1.39x * lammps_HECBioSim_465k: ~1.46x * lammps_HECBioSim_61k: ~1.49x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 3.84 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: TVOT1003E BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-144: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Number of Atoms) of this benchmark for a 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source lammps 20220623. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * lammps_HECBioSim_1400k: ~1.72x * lammps_HECBioSim_20k: ~1.44x * lammps_HECBioSim_3000k: ~1.72x * lammps_HECBioSim_465k: ~1.73x * lammps_HECBioSim_61k: ~1.56x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 (384 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: RVOT1000C BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-145: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (ns/day) of this benchmark for a 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source NAMD 2.15alpha2. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * namd-stmv20M: ~1.41x * namd-apoa1: ~1.50x * namd-f1atpase: ~1.29x * namd-stmv: ~1.41x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: TVOT1003E BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-146: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (ns/day) of this benchmark for a 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source NAMD 2.15alpha2. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * namd-stmv20M: ~1.20x * namd-apoa1: ~1.02x * namd-f1atpase: ~1.50x * namd-stmv: ~1.10x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 (384 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: RVOT1000C BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-147: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Elapsed Time) of this benchmark for a 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered system production running select tests on Open-Source quantum_espresso 7.1. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * qe-7.0_Ausurf: ~1.17x * qe-7.0_Ta205: ~1.22x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: TVOT1003E BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-148: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Elapsed Time) of this benchmark for a 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source quantum_espresso 7.1. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * qe-7.0_Ausurf: ~1.29x * qe-7.0_Ta205: ~1.14x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 (384 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 3.84 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: RVOT1000C BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-149: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Mean Time/Step) of this benchmark for a 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source WRF® 4.3.3. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * wrf-2.5: ~1.19x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 128-Core AMD EPYC™ 9755 (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZVL2512HCJQ-00B00 512.11 GB NVMe Platform and BIOS: TVOT1003E BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-150: AMD testing as of 04/02/2025. The detailed results show the average uplift of the performance metric (Mean Time/Step) of this benchmark for a 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 powered reference system compared to a 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P powered production system running select tests on Open-Source WRF ® 4.3.3. Uplifts for the performance metric normalized to the Intel® Xeon® 6980P follow for each benchmark: * wrf-2.5: ~1.15x System Configurations CPU: 2P Intel® Xeon® 6980P (256 total cores) Memory: 24x 96 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SOLIDIGM SBFPF2BU076T 7.68 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: 1.0 BIOS Options: SMT=OFF, SNC=3, HPC Workload Profile OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: BOOT_IMAGE=(hd1,gpt2)/vmlinuz-5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 crashkernel=1G-4G:192M,4G-64G:256M,64G-:512M rhgb mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 intel_pstate=disable processor.max_cstate=1 intel_idle.max_cstate=0 iommu=pt Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag CPU: 2P 192-Core AMD EPYC™ 9965 (384 total cores) Memory: 24x 64 GB DDR5-6400 Storage: SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 3.84 TB NVMe Platform and BIOS: RVOT1000C BIOS Options: SMT=Off NPS=4 Power Determinism Mode OS: rhel 9.4 5.14.0-427.16.1.el9_4.x86_64 Kernel Options: amd_iommu=on iommu=pt mitigations=off tsc=nowatchdog nmi_watchdog=0 Runtime Options: cpupower idle-set -d 2 cpupower frequency-set -g performance echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/nmi_watchdog echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/numa_balancing echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled echo 'always' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag Results may vary based on system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-151: TPCxAI @SF30 Multi-Instance, 32C Instance Size throughput results based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025 running multiple VM instances. The aggregate end-to-end AI throughput test is derived from the TPCx-AI benchmark and as such is not comparable to published TPCx-AI results, as the end-to-end AI throughput test results do not comply with the TPCx-AI Specification. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (6067.53 Total AIUCpm, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (4073.42 Total AIUCpm, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (3550.50 Total AIUCpm, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings. TPC, TPC Benchmark, and TPC-H are trademarks of the Transaction Processing Performance Council.
- 9xx5-152A: Deepseek-R1-617B throughput results based on AMD internal testing as of 01/28/2025. Configurations: llama.cpp framework, 1.58 bit quantization (UD_IQ1_S, MoE at 1.56 bit), batch sizes 1 and 4, 16C Instances, Use Case Input/Output token configurations: [Chatbot = 128/128, Essay = 128/1024, Summary = 1024/128, Rewrite = 1024/1024]. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, reference system, 3TB 24x128GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic), SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, reference system, 3TB 24x128GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 22.04.3 LTS | 5.15.0-105-generic), SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, production system, 3TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS | 6.13.2-061302-generic, SMT=ON, Performance Bias, Mitigations=on) Results: BS=1 6980P 9755 9965 Rel9755 Rel9965 Chatbot 47.31 61.88 70.344 1.308 1.487 Essay 42.97 56.04 61.608 1.304 1.434 Summary 44.99 59.39 62.304 1.32 1.385 Rewrite 41.8 68.44 55.08 1.637 1.318 BS=4 6980P 9755 Rel9755 Rel9965 Chatbot 76.01 104.46 143.496 1.374 1.888 Essay 67.89 93.68 116.064 1.38 1.71 Summary 70.88 103.39 99.96 1.459 1.41 Rewrite 65 87.9 78.12 1.352 1.202 Results may vary due to factors including system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-153: Memcached™ results based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (122,462,350 Operations/sec, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (101,861,436 Operations/sec, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (45,547,949 Operations/sec, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-154: MongoDB® results based on AMD internal testing as of 04/01/2025. 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (4,137,521 Operations/sec, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (3,612,687 Operations/sec, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (2,569,278 Operations/sec, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=ON, Performance bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.
- 9xx5-155: Monte Carlo results based on AMD internal testing as of 04/30/2025. Workload Configs: ICC+MKL v2025.1, European Option Pricing, 800 Options, throughput in options/s 2P AMD EPYC 9965 (1,147,078.36 options/s, 384 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910), 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu® 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=OFF, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P AMD EPYC 9755 (872,204.70 options/s, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, AMD reference system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 2 x 40 GbE Mellanox CX-7 (MT2910) 3.84TB Samsung MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=OFF, Determinism=power, Mitigations=on) 2P Intel Xeon 6980P (760,193.98 options/s, 256 Total Cores, 500W TDP, Production system, 1.5TB 24x64GB DDR5-6400, 4 x 1GbE Broadcom NetXtreme BCM5719 Gigabit Ethernet PCIe 3.84TB SAMSUNG MZWLO3T8HCLS-00A07 NVMe, Ubuntu 24.04 LTS kernel 6.13, SMT=OFF, Performance bias, Mitigations=on) Results may vary based on factors including but not limited to system configurations, software versions, and BIOS settings.