Performance Briefs and Tech Docs
Find the technical resources you need to build your infrastructure with AMD EPYC 9005 server CPUs

Advancing AI, Cloud, and Enterprise Computing

AMD EPYC™ 9005 server CPUs provide end-to-end AI performance.
AMD EPYC™ 9005 CPUs can match integer performance of legacy hardware with up to 88% fewer racks2, dramatically reducing physical footprint, power consumption, and the number of software licenses needed, freeing up space for new or expanded AI workloads.
Many AI workloads—language models with 13 billion parameters and below, image and fraud analysis, or recommendation systems run efficiently on CPU-only servers that feature AMD EPYC™ 9005 CPUs. Servers running two 5th Gen AMD EPYC 9965 CPUs offer up to 2x inference throughput when compared to previous generation offerings.3
The AMD EPYC™ 9005 family includes options that are optimized to be host-CPUs for GPU-enabled systems to help increase performance on select AI workloads and improve the ROI of each GPU server. For example, in geomean inference performance tests across 8 models and 4 use cases, a high‑frequency AMD EPYC 9575F CPU-based server with 8 GPUs delivers up to 13% faster time‑to‑first‑token and 6.6% higher overall inference throughput than an equivalent 8 GPU server powered by Intel Xeon 6960P CPUs.4,5,6
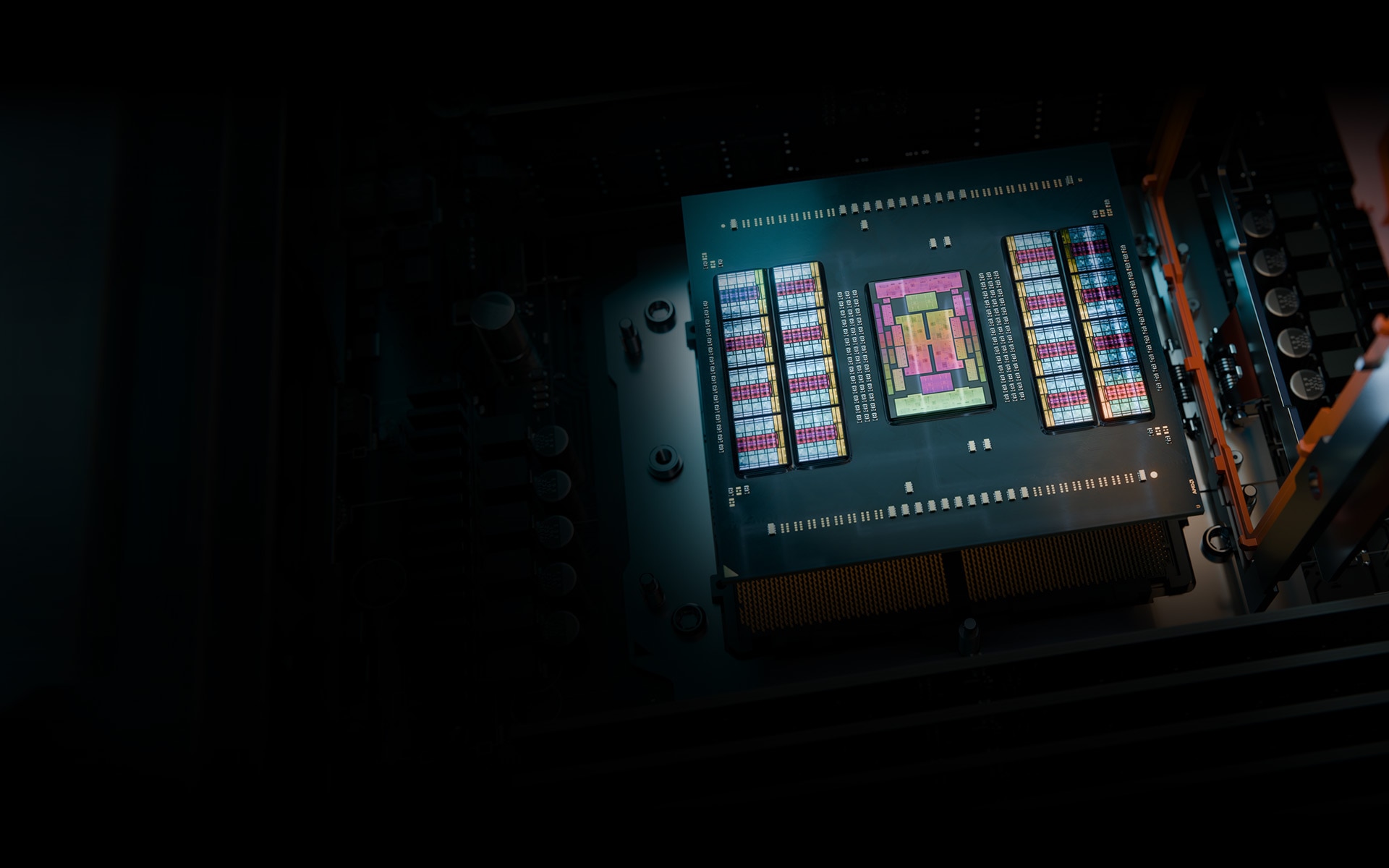
AMD EPYC 9005 server CPUs deliver exceptional performance while enabling leadership energy efficiency and cost-of-ownership (TCO) value in support of key business imperatives.
AMD EPYC 9005 CPU-powered servers leverage the new “Zen 5” cores to offer compelling mainstream performance metrics, including 2.3x the integer performance when compared to leading competitive offerings.7
AMD EPYC™ 9005 server CPUs provide density and performance for cloud workloads. With 192 cores, the top-of-stack AMD EPYC 9965 processor will support 33% more virtual CPUs (vCPUs) than the leading available Intel® Xeon 6E “Sierra Forest” 144 core processor (1 core per vCPU).
Data centers are demanding more energy than ever. AMD EPYC™ 9005 server CPUs continue to provide the energy efficiency and TCO benefits found in previous AMD EPYC generations.

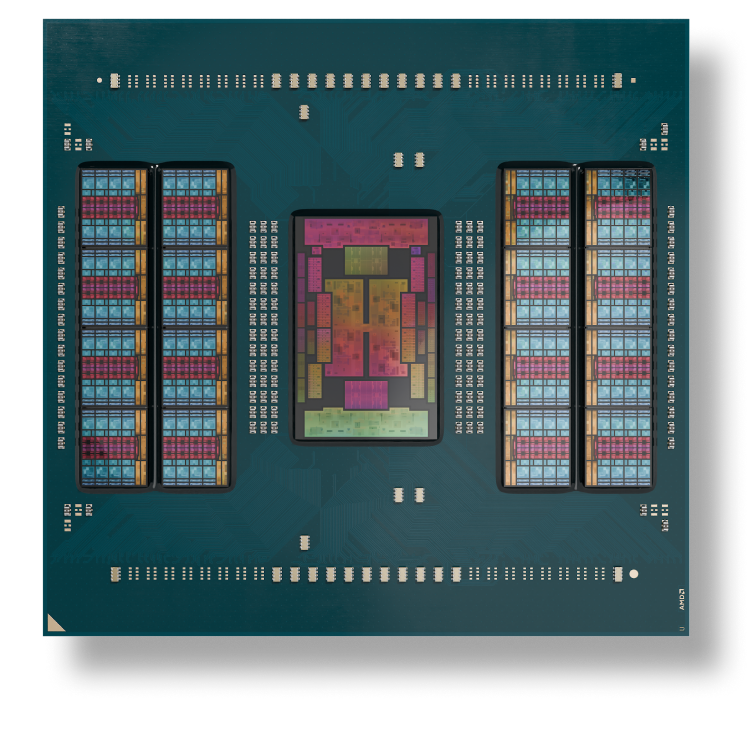
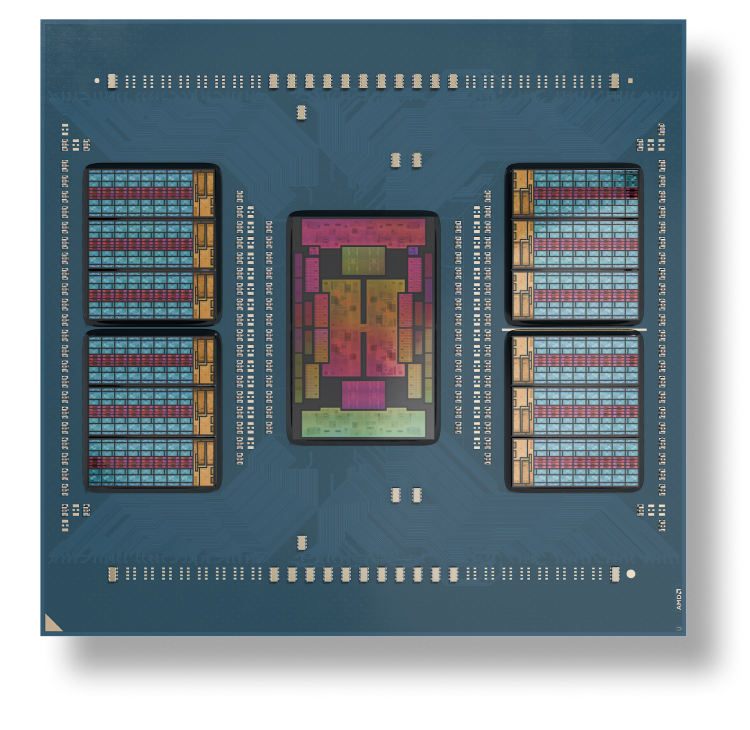
AMD EPYC 9005 Series server CPUs include up to 192 “Zen 5” or “Zen 5c” cores with exceptional memory bandwidth and capacity. The innovative AMD chiplet architecture enables high performance, energy-efficient solutions optimized for your different computing needs.