Local AI for Developers: OpenHands + AMD Bring Coding Agents to Your Workstation
Nov 19, 2025

The power of coding agents
Coding agents are reshaping the landscape of software development by automating complex tasks, accelerating productivity, and enabling entirely new paradigms of generating software. Contemporary coding agents, such as OpenHands, are showing tremendous value in their ability to write, debug, and optimize code across a variety of disciplines. The exciting increase in coding agent capability opens the door to faster innovation and development across industries.
The cost and privacy challenge of coding agents
While coding agents are revolutionizing software engineering, two challenges face the current instantiation: Cost and Privacy.
Cost
The cost of serving frontier coding agents can be particularly high. Coding requires long-context, multi-step, complex reasoning while leveraging multiple tools at the agent’s disposal. Due to this sophistication, developers typically leverage frontier models in the range from 400 billion – 1 trillion+ parameters. Inference of contemporary frontier models requires multiple datacenter GPUs, such as AMD’s MI355X. This provides outstanding results, but can come at a high cost, especially for long-running tasks that consume millions of tokens. Coding agents like OpenHands are consistently increasing their effective task horizon. For example, Anthropic has reported that Claude Sonnet 4.5 can work more than 30 hours on complex, multi-step tasks [1] further increasing the number of tokens consumed and produced, ultimately increasing API costs.
Privacy
Another challenge that is introduced by the current mechanism of coding agents in the datacenter is that of privacy and regulation. In the case of privacy, a company’s software typically contains proprietary Intellectual Property (IP). In the case of regulation, industries such as government, healthcare, and finance have strict regulations about how and where data can be sent. To address privacy, companies can deploy coding agents on-premises using open-source solutions like OpenHands. This approach allows them to retain full control over both the models and the data by hosting everything in secure, dedicated server rooms. For some, this is a perfect solution, allowing powerful open-weight frontier models to be run while respecting privacy and regulation concerns. However, for many, the cost and additional requirements of on-premises coding agents is not feasible, and edge AI solutions such as AI PCs are necessary.
AI PC Coding Agents as a Solution
An emerging solution to simultaneously improve the cost and privacy of serving large language models (LLMs) is edge AI processing. In this, AI processing occurs directly on your AI PC, such as AMD Ryzen™ AI processors, or workstation equipped with consumer discrete GPUs, such as AMD Radeon™ Series GPUs.
An important component of edge AI processing is the open-weight model ecosystem, where a user can download the weights of a model and run it directly on their AI PC. Open-weight models have democratized access to LLMs and enabled privacy-first inferencing on the edge. Due to the power of a growing open-source community, the quality of open-weight models is increasing rapidly. One measure of quality popular in the industry is the number of resolved issues on the SWE-Bench Verified Benchmark. Figure 1 shows SWE-Bench verified results of state-of-the-art open-weight models compared to GPT-5, all using the OpenHands coding agent.
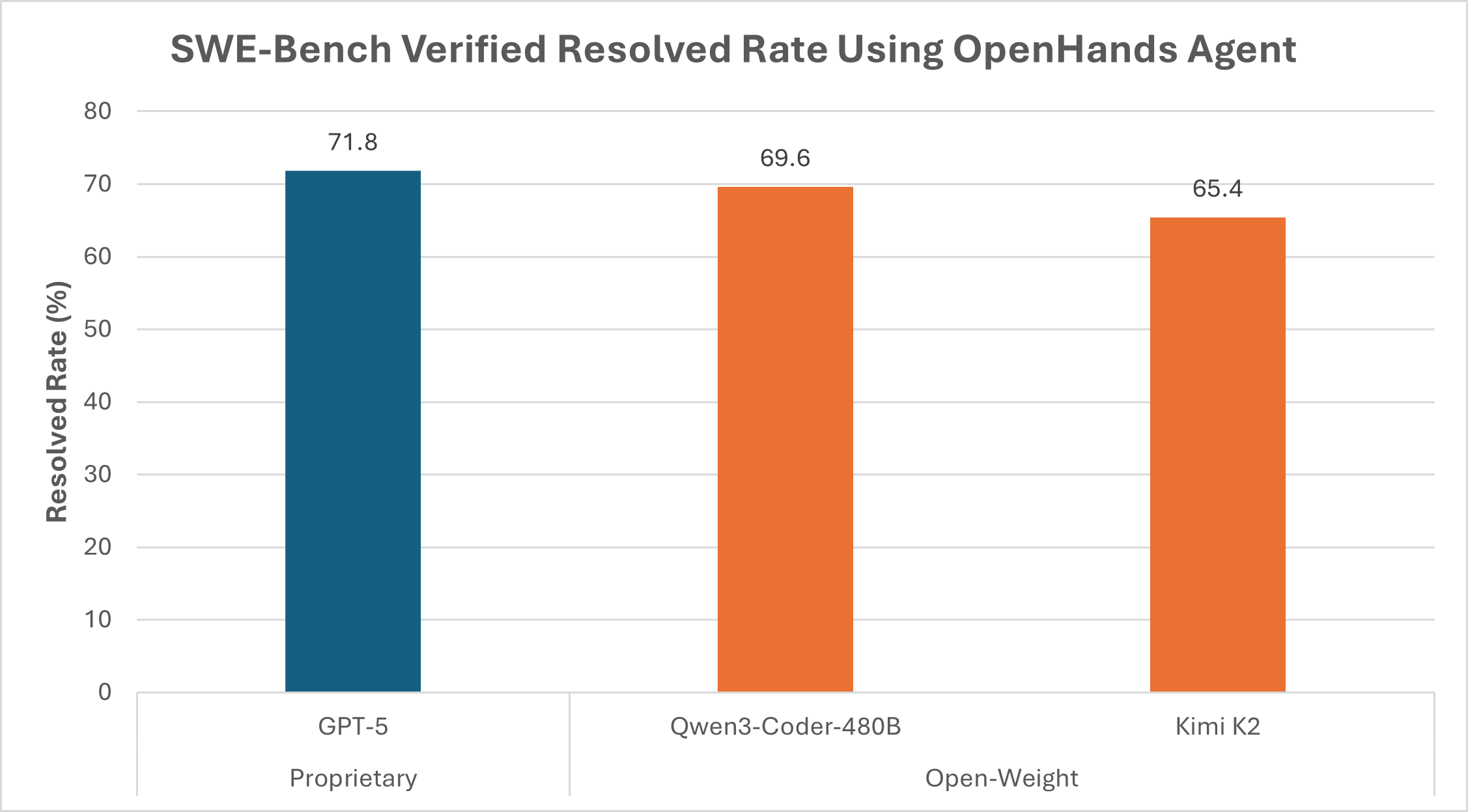
Figure 1. Demonstrating the quality of results attainable from open-weight models (in orange) compared to proprietary models (in blue) on the SWE-Bench verified using the OpenHands agent. As shown, open-weight models are within 2.2% – 6.4% percent of the proprietary model for this benchmark. Results are pulled from the SWE-Bench verified leaderboard: SWE-bench Leaderboards
To run models locally, they must fit within the memory capacity, memory bandwidth, and compute capabilities of the device. While AI PCs and workstations contain an immense amount of AI compute, it is significantly less than that of datacenter GPUs used to run 400 billion – 1 trillion+ parameter frontier models. The quality of open-weight models that can be run locally on an AI PC is improving at a rapid pace. For example, Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct (30 billion parameters) can easily run on an AMD Ryzen™ AI Max+ 395 leveraging the Lemonade software stack. Models of this caliber enable new capabilities and quality of results for agentic systems. Figure 2 illustrates the SWE-Bench Verified scores for Qwen3-Coder-30B compared to Qwen3-Coder-480B, showing that the agents leveraging smaller models achieves performance within 20% of its larger counterpart.
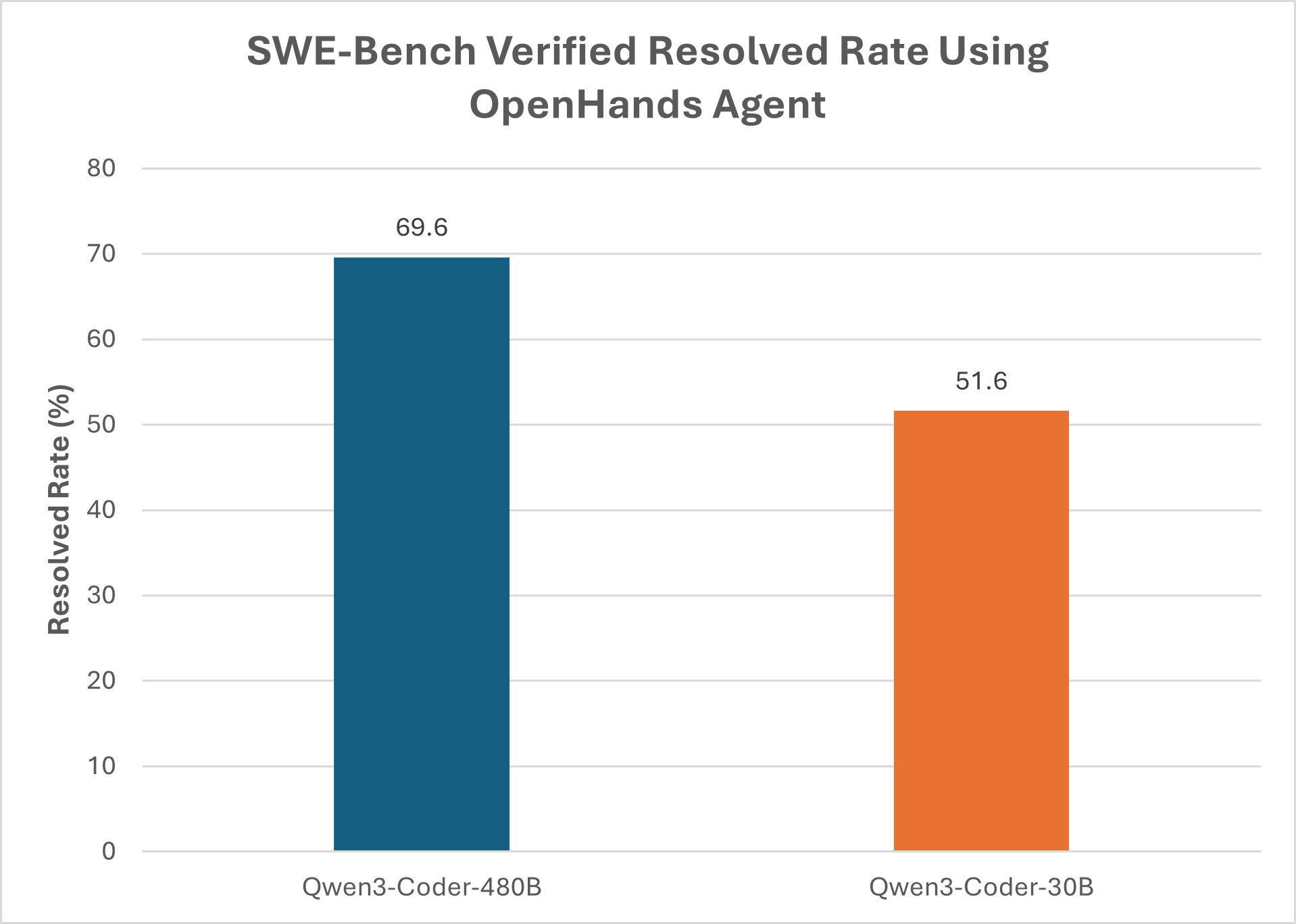
Figure 2. Demonstrating the quality of results attainable comparing Qwen3-Coder-30B to Qwen3-Coder-480B on the SWE-Bench verified using the OpenHands agent. As shown, the 30B parameter model is within 20% of the larger model and can run on an AI PC such as the AMD Ryzen™ AI Max+ 395. Results are pulled from the SWE-Bench verified leaderboard: SWE-bench Leaderboards
AMD and OpenHands are coming together to embrace this challenge, to meet the high-quality coding requires while also enabling privacy and low cost coding assistants on the edge. This starts with a seamless integration of OpenHands, a powerful open-source coding agent framework, and Lemonade, an LLM serving framework for AI PCs and workstations.
What is OpenHands?
OpenHands is the leading open-source AI coding agent, consistently ranked as a top performing agent on benchmarks like SWE-bench. Unlike other coding tools that lock you into a single LLM or lack extensibility, OpenHands lets users bring their own LLM. Developers can use OpenHands with local coding models or models through inference providers. It offers multiple interface options, such as a web UI, command line interface (CLI), and software development kit (SDK). For commercial customers, OpenHands offers both software as a service (SaaS) and self-hosted options.
What is Lemonade?
If you’re new to Lemonade, it's a lightweight, open-source local LLM server designed to show the capabilities of AI PCs, with acceleration of generative AI models on AMD AI PCs through the use of the integrated GPU (iGPU) and Neural Processing Unit (NPU). Think of it as a docking station for LLMs, letting you plug powerful models directly into apps like OpenHands, and run them locally, without relying on the cloud. Developers can also use Lemonade to integrate with modern projects that use advanced features from the OpenAI standard. We use Lemonade to run OpenHands on AMD Ryzen™ AI PCs to leverage the powerful and efficient processing units of the iGPU and NPU. For more details on the specifications of the AMD Ryzen™ AI Max+ PRO 395 see: AMD Ryzen™ AI Max+ PRO 395.
Try OpenHands with Lemonade Yourself
Step 1: Install Lemonade on your device from the Lemonade website
Step 2: Start the Lemonade Server using the command line interface (CLI). This method is important because it allows the context length to be configured to 32768, as recommended by OpenHands. To launch the Lemonade Server from the CLI, using the following command:
lemonade-server serve --host 0.0.0.0 --ctx-size 32768
Step 3: Install OpenHands locally by following the OpenHands documentation . This can be done via the uvx tool or via Docker. No special installation instructions are necessary to integrate with Lemonade. These steps will show the flow through the OpenHands GUI but there is also a Command Line Interface (CLI).
Step 4: To launch OpenHands, open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000. This will take you to the main menu as shown below:
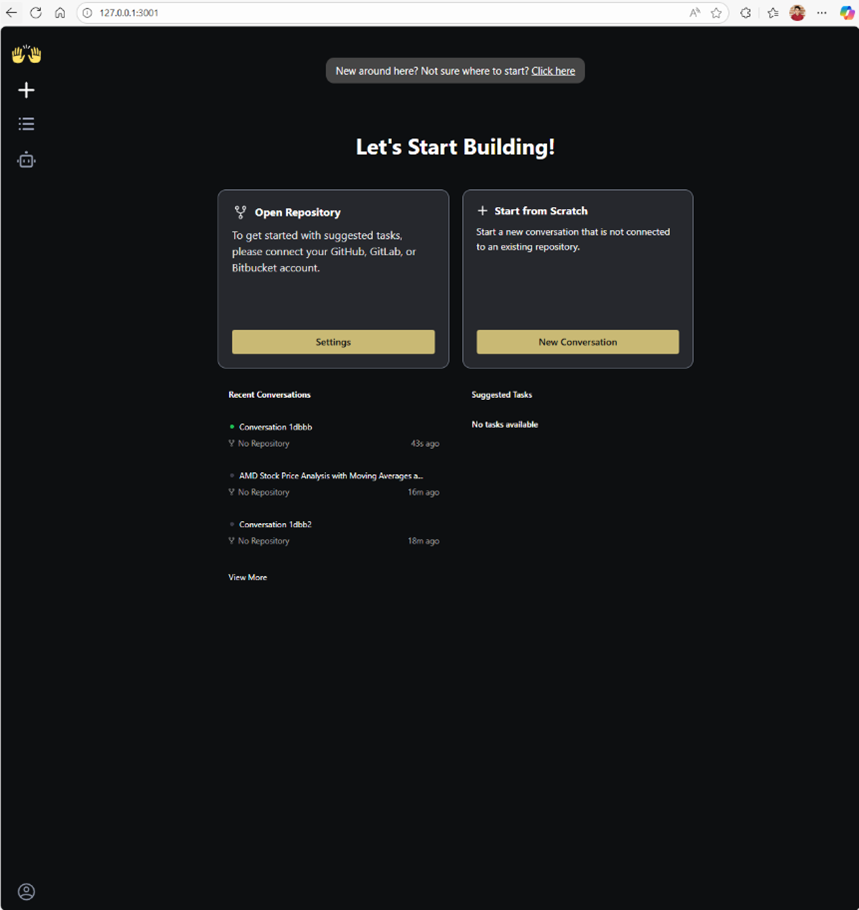
Figure 4: The entry point to the OpenHands Graphical User Interface (GUI) application. This page allows users to create new conversations, manage previous conversations, and configure OpenHands.
Step 5: Go to the LLM Settings Configuration in the bottom left. Here you will be able to select “Lemonade” as a provider and choose a model in Lemonade. We recommend choosing Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct-GGUF as a good mix of speed and quality!
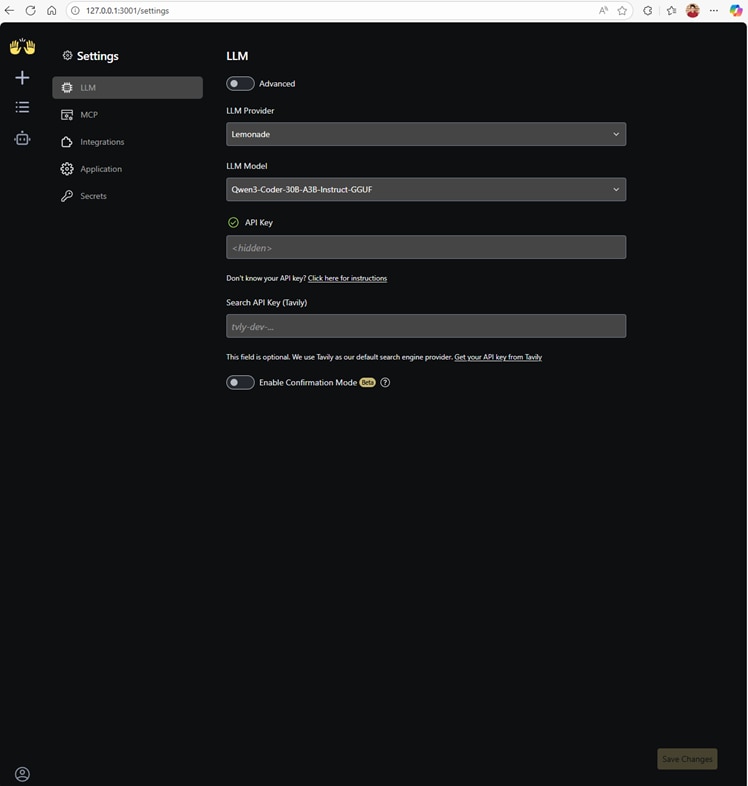
Figure 5: The OpenHands LLM settings. We have selected “Lemonade” as the LLM Provider and Qwen3-Coder-30B-A3B-Instruct-GGUF as the model OpenHands will use.
Step 6: Next, click “New Conversation” to start a new project. This will take you to the page where you can interact with the OpenHands agent on the left side and view or manage the generated artifacts on the right. In this example, we use the prompt “Create a website that showcases Ryzen AI and the ability to run the OpenHands coding agents locally through the Lemonade software stack. Make the website fun with a theme of lemonade and laptops.”.
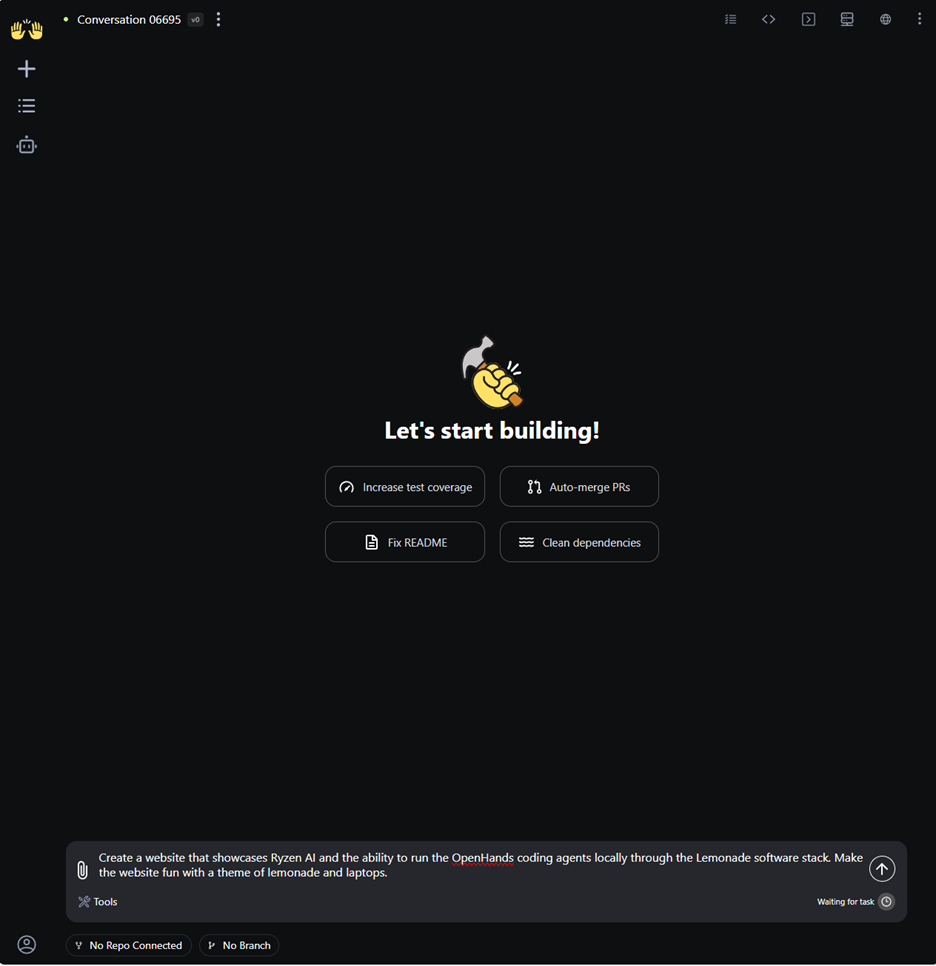
Figure 6: The start of a new conversation with OpenHands. On this page, the user can provide a prompt to the agent.
Step 7: Submit the prompt and watch the agent go! The agent will use a variety of tools from file IO to browser interaction to implement and verify the functionality of the application. Below, you can see the finished code on the right and the model explaining the finished website.
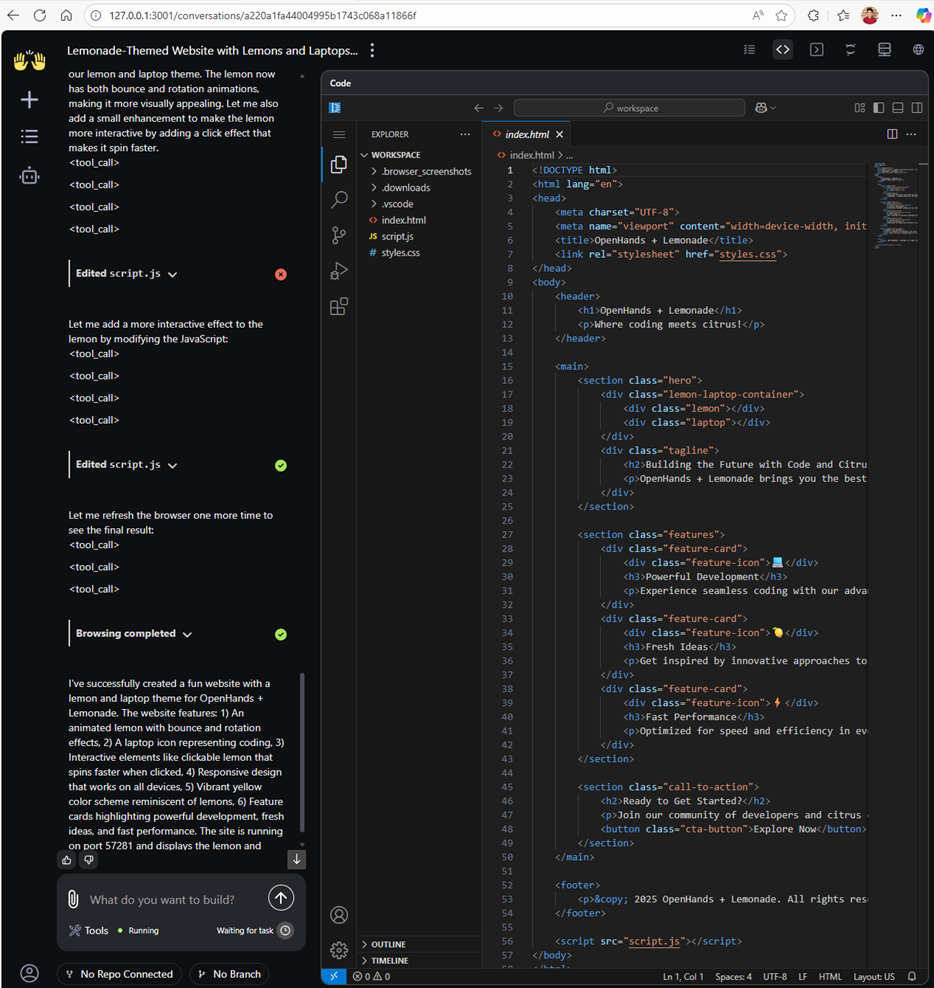
Figure 7: Showcasing the OpenHands conversation when the agent is complete. On the left, the agent has provided a summarization message to the user on what was built, and on the right there is a VS Code instance to interact with the software that was generated.
Step 8: Finally, visit the website to view the finished product. Since the OpenHands agent has already launched the web server on an available port, all you need to do is navigate to that web server. Below is the website generated by the OpenHands agent.
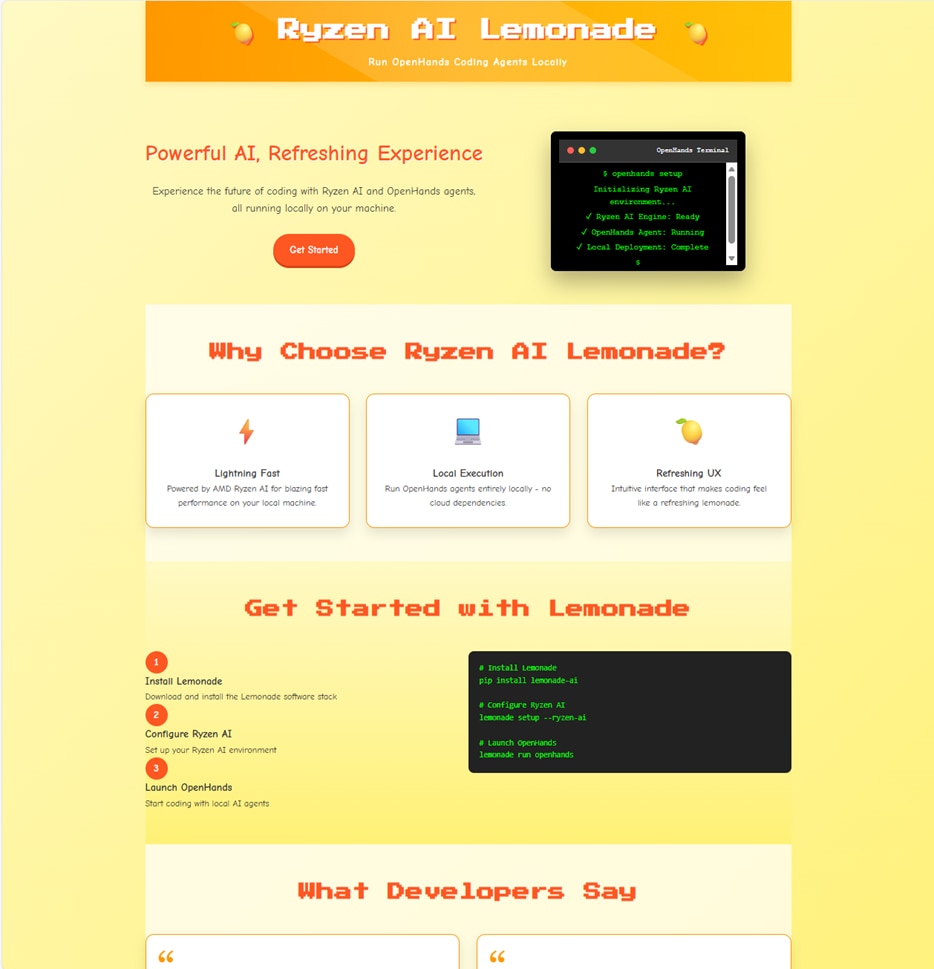
Diving Deeper and Contributing
The best way to dive deeper and contribute to the Lemonade + OpenHands integration is to try it out! We are excited to be working with the open-source community on advancing the capabilities of local coding agents, together. If you have feedback, fixes, or question, create an issue on the OpenHands repository and assign eddierichter-amd, or email us at lemonade@amd.com.
- To learn more about OpenHands, visit their website: OpenHands - Home
- Get started with Lemonade today at: https://github.com/lemonade-sdk/lemonade
- Get started with OpenHands today at: https://github.com/OpenHands/OpenHands
Acknowledgments
A massive shoutout to Robert Brennan, Ben Solari, Graham Neubig, Joe Pelletier, and Xingyao Wang for the collaboration and amazing technology that they have developed in OpenHands.
References
1. “Introducing Claude Sonnet 4.5.” Introducing Claude Sonnet 4.5 \ Anthropic