Remove Hurdles from Technical Computing Workloads
When it comes to technical computing, speed is key. Time to market is a hurdle customers need to overcome, and high-performance computing (HPC) servers shouldn’t slow them down. Latency, bandwidth, bottlenecks, and long optimization times; these factors hold customers back from faster iteration and testing, increasing costs and wasting resources.
Customers commonly face these bottlenecks:
- Limits: Some workloads never seem to get enough performance from each core.
- Latency: Lower is better, but it never seems to be low enough for high-data-volume applications.
- Time: Optimizing and rearchitecting takes time; time customers don’t have.
- Resources: Same workload, fewer resources. Or a bigger workload with the same resources. There’s simply not enough bandwidth to go around.
With the launch of 4th Gen AMD EPYC™ processors with AMD 3D V-Cache™ technology, those restrictions can now be addressed.
Technical Computing at Speed
4th Gen AMD EPYC processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology are designed to solve today’s problems, now. The world’s highest performing x86 CPU for technical computing delivers up to 96 cores, 128 PCIe® lanes, and 12-channel DDR5 memory support.1 Plus, with AMD 3D V-Cache technology, customers can distribute 1152MB of L3 cache across their workloads for unrivaled performance and low latency across Electronic Design Automation (EDA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF), and other complex technical workloads.
The result for users? Leadership performance over competitor products, delivering up to 2.9x max performance among ANSYS simulations for processors with 32 cores and at the top of stack:
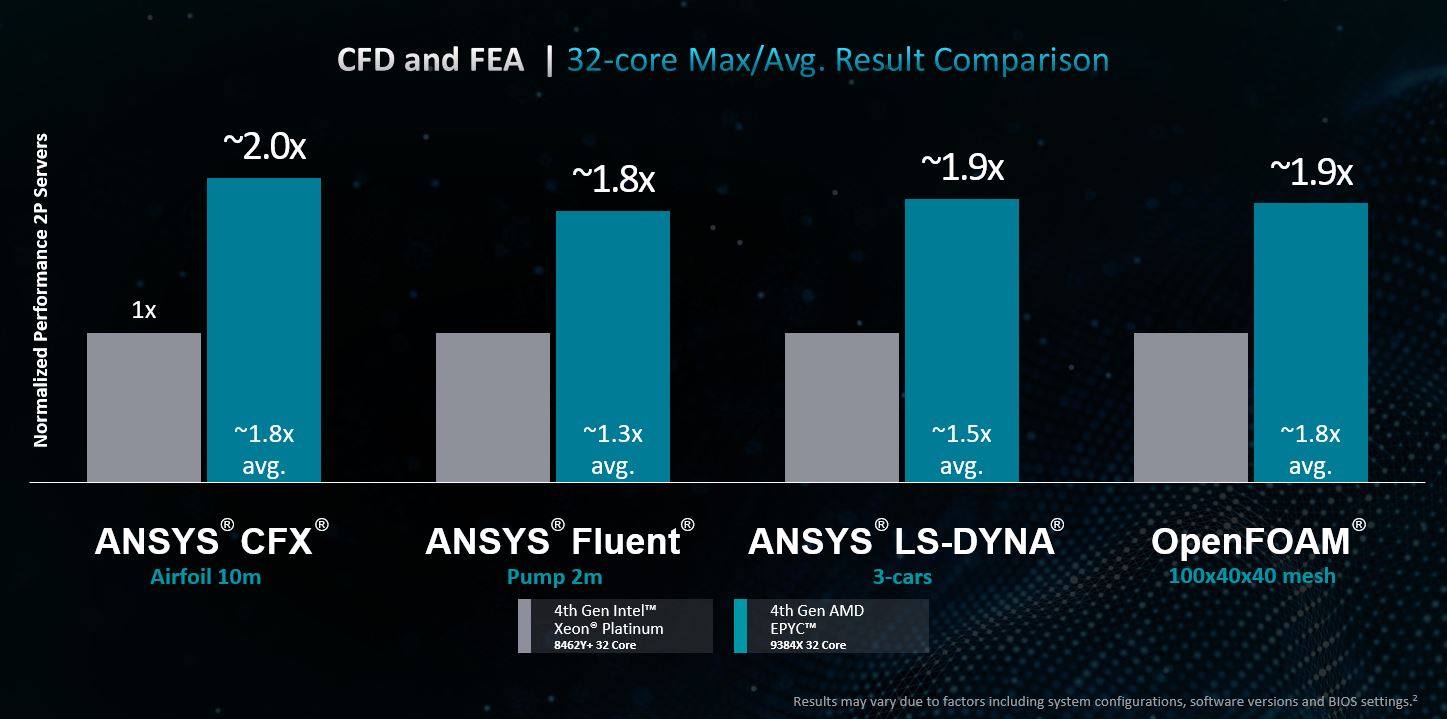
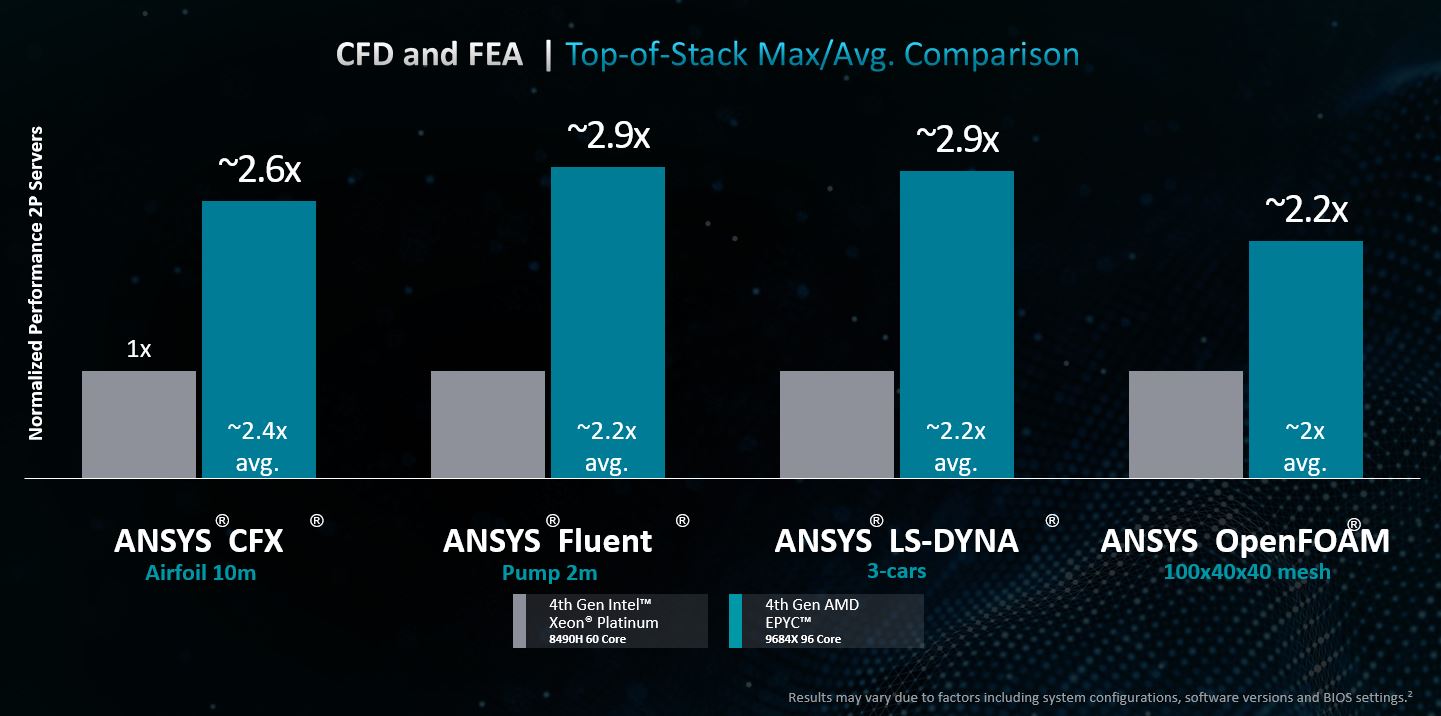
These new AMD EPYC™ processors enable customers to get their products to market faster, delivering advanced capabilities that streamline design and product development, so products are on shelf sooner. Software is backed by hardware that can lead to cost-saving opportunities, the achievement of business goals with rapid modeling, and insights to improve designs and better predict outcomes.
4th Gen AMD EPYC processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology do all of this while leaving room to enable increases in server efficiency, lower TCO, and deliver more performance from the same or less data center power. That means customers can get the same level of performance with a smaller server footprint, ideal for reducing the amount of infrastructure needed, while also reducing associated CO2 emissions.
And upgrading is easy. The new AMD EPYC processors work right out of the box with existing x86 software, allowing time to be spent empowering business, rather than complex redeployments.
State-of-the-art security in the form of AMD Infinity Guard means customers adopting these new CPUs enjoy capabilities that decrease potential attack surfaces as software boots, executes, and processes critical data. Confidential computing solutions enabled by AMD Infinity Guard can defend against threats and guard your data on-prem or in the cloud.3
HPC is revolutionizing innovation across industries. Customers who use 4th Gen AMD EPYC processors with AMD 3D V-Cache technology can overcome technical workload obstacles. Contact your AMD representative now to learn more.
AMD Arena
Enhance your AMD product knowledge with training on AMD Ryzen™ PRO, AMD EPYC™, AMD Instinct™, and more.
Subscribe
Get monthly updates on AMD’s latest products, training resources, and Meet the Experts webinars.

Related Articles
Related Training Courses
Related Webinars
Footnotes
- SP5-165 - The EPYC 9684X CPU is the world’s highest performance x86 server CPU for technical computing, comparison based on SPEC.org publications as of 6/13/2023 measuring the score, rating or jobs/day for each of SPECrate®2017_fp_base (SP5-009E), Altair AcuSolve (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-altair-acusolve.pdf), Ansys Fluent (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-fluent.pdf), OpenFOAM (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-openfoam.pdf), Ansys LS-Dyna (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-ls-dyna.pdf), and Altair Radioss (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-altair-radioss.pdf) application test case simulations average speed up on 2P servers running 96-core EPYC 9684X vs top 2P performance general-purpose 56-core Intel Xeon Platinum 8480+ or top-of-stack 60-core Xeon 8490H based server for technical computing performance leadership. “Technical Computing” or “Technical Computing Workloads” as defined by AMD can include: electronic design automation, computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, seismic tomography, weather forecasting, quantum mechanics, climate research, molecular modeling, or similar workloads. Results may vary based on factors including silicon version, hardware and software configuration and driver versions. SPEC®, SPECrate® and SPEC CPU® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- As of 6/13/2023, Sources: ANSYS CFX https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-cfx.pdf, ANSYS LS-DYNA https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-ls-dyna.pdf, ANSYS Fluent https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-fluent.pdf and OpenFOAM https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-openfoam.pdf.
- AMD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC Processor generations. Infinity Guard security features on AMD EPYC processors must be enabled by server OEMs and/or cloud service providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. Learn more about Infinity Guard at https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard. GD-183
- SP5-165 - The EPYC 9684X CPU is the world’s highest performance x86 server CPU for technical computing, comparison based on SPEC.org publications as of 6/13/2023 measuring the score, rating or jobs/day for each of SPECrate®2017_fp_base (SP5-009E), Altair AcuSolve (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-altair-acusolve.pdf), Ansys Fluent (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-fluent.pdf), OpenFOAM (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-openfoam.pdf), Ansys LS-Dyna (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-ls-dyna.pdf), and Altair Radioss (https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-altair-radioss.pdf) application test case simulations average speed up on 2P servers running 96-core EPYC 9684X vs top 2P performance general-purpose 56-core Intel Xeon Platinum 8480+ or top-of-stack 60-core Xeon 8490H based server for technical computing performance leadership. “Technical Computing” or “Technical Computing Workloads” as defined by AMD can include: electronic design automation, computational fluid dynamics, finite element analysis, seismic tomography, weather forecasting, quantum mechanics, climate research, molecular modeling, or similar workloads. Results may vary based on factors including silicon version, hardware and software configuration and driver versions. SPEC®, SPECrate® and SPEC CPU® are registered trademarks of the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. See www.spec.org for more information.
- As of 6/13/2023, Sources: ANSYS CFX https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-cfx.pdf, ANSYS LS-DYNA https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-ls-dyna.pdf, ANSYS Fluent https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-ansys-fluent.pdf and OpenFOAM https://www.amd.com/system/files/documents/amd-epyc-9004x-pb-openfoam.pdf.
- AMD Infinity Guard features vary by EPYC Processor generations. Infinity Guard security features on AMD EPYC processors must be enabled by server OEMs and/or cloud service providers to operate. Check with your OEM or provider to confirm support of these features. Learn more about Infinity Guard at https://www.amd.com/en/technologies/infinity-guard. GD-183




